GS-9674 in NASH: a phase 2 study
Patel K, AASLD 2018, Abs. 736
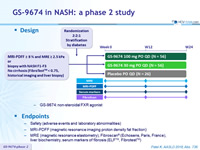
Design
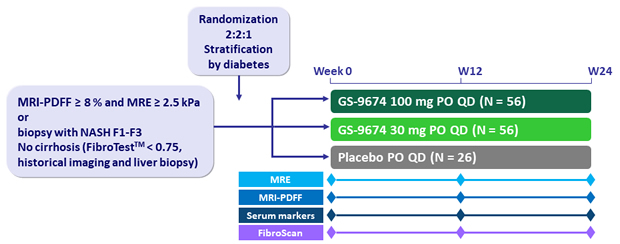
-
GS-9674: non-steroidal FXR agonist
Endpoints
- Safety (adverse events and laboratory abnormalities
- MRI-PDFF (magnetic resonance imaging proton density fat fraction)
- MRE (magnetic resonance elastometry), Fibroscan® (Echosens, Paris, France), liver biochemistry, serum markers of fibrosis (ELFTM, FibrotestTM)
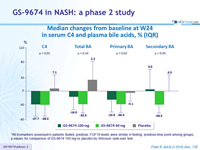
Median changes from baseline at W24 in serum C4 and plasma bile acids, % (IQR)
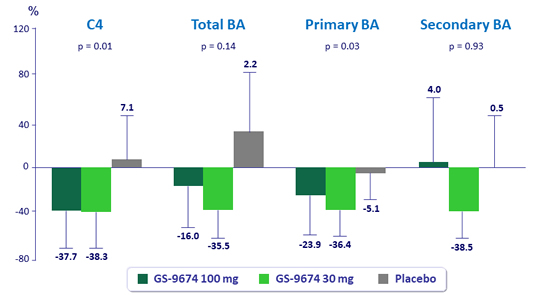
*All biomarkers assessed in patients fasted, predose; FGF19 levels were similar in fasting, predose time point among groups; p-values for comparison of GS-9674 100 mg vs placebo by Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
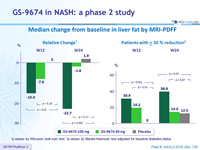
Median change from baseline in liver fat by MRI-PDFF
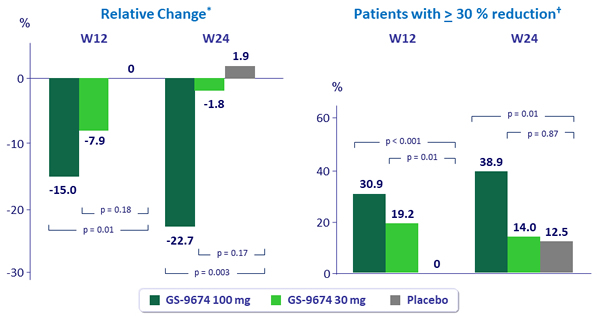
*p-values by Wilcoxon rank-sum test; †p-values by Mantel-Haenszel test adjusted for baseline diabetes status.
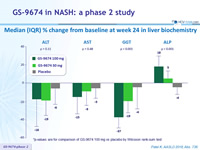
Median (IQR) % change from baseline at week 24 in liver biochemistry
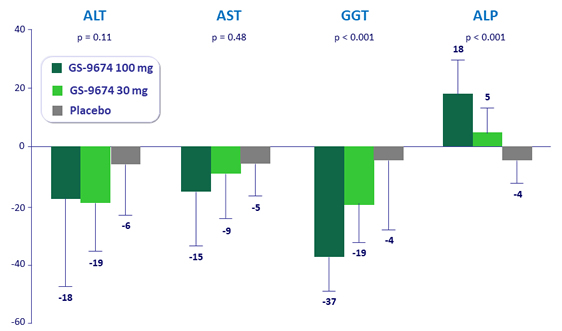
*p-values are for comparison of GS-9674 100 mg vs placebo by Wilcoxon rank-sum test
Summary
- Significant improvements in hepatic steatosis and liver biochemistry and reductions in serum bile acids in patients with NASH
- GS-9674 was well tolerated:
- Changes in serum lipids and glycemic parameters were not observed
- Grade ≥ 2 pruritus was more common in patients treated with GS-9674 100 mg but only one patient discontinued treatment due to pruritus
- Phase 2 ATLAS study ongoing in patients with F3-F4 fibrosis due to NASH