NASH: A Summary
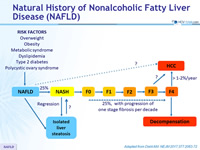
Natural History of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
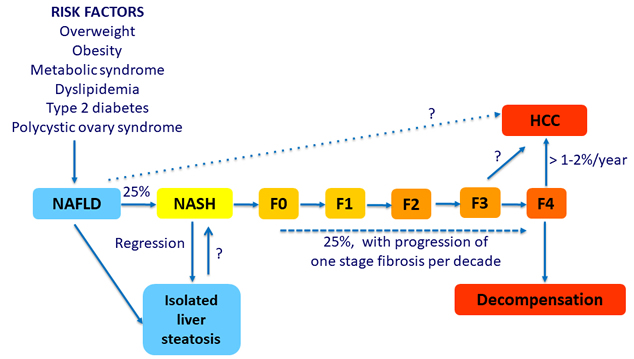
Adapted from Diehl AM. NEJM 2017;377:2063-72
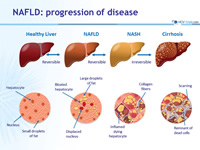
NAFLD: progression of disease
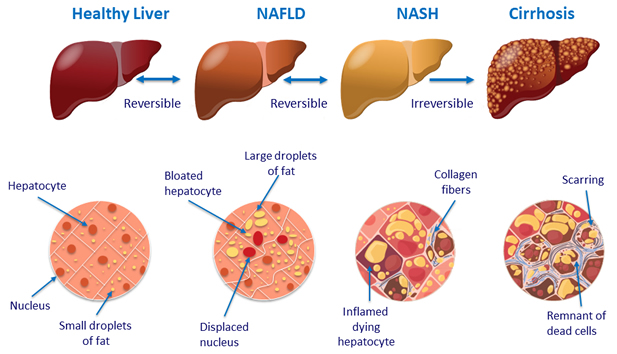
Liver histology in NAFLD
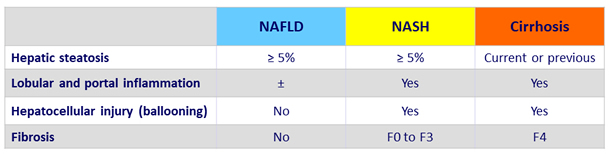
Histology scoring
- NAS (NAFLD Activity Score), reflects disease activity: unweighted composite of
- Steatosis (0 to 3)
- Lobular inflammation (0 to 3)
- Ballooning (0 to 2)
- SAF Score: semi-quantitative score of
- Steatosis (0 to 3)
- Activity (lobular inflammation + ballooning) = NAS (0 to 8)
- Fibrosis (0 to 4)
Adapted from Chalasani N. Practice Guidance from the AASLD;Hepatology 2018;67:328-357
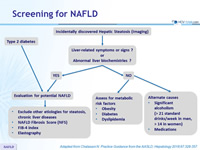
Screening for NAFLD
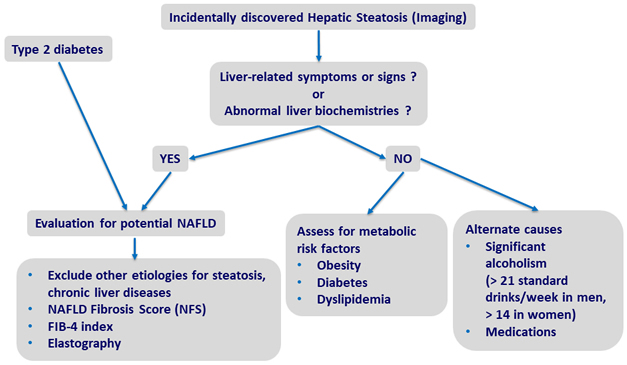
Adapted from Chalasani N. Practice Guidance from the AASLD;Hepatology 2018;67:328-357
Non-invasive Scores of NAFLD
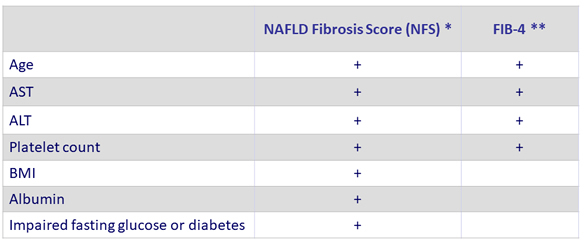
* NFS: www.mdcalc.com/nafld-non-alcoholic-fatty-liver-disease-fibrosis-score or gihep.com/calculators/hepatology/nafld-fibrosis-score
** FIB-4: www.mdcalc.com/fibrosis-4-fib-4-index-liver-fibrosis or gihep.com/calculators/hepatology/fibrosis-4-score
Assessment of NAFLD
- Non invasive evaluation
- Presence of metabolic syndrome: predictive of steatosis > LIVER BIOPSY
- NFS*, FIB-4, vibration controlled transient elastography, magnetic resonance elastography: predictive of advanced fibrosis > LIVER BIOPSY
- Serum ferritin and iron saturation: if high, marker of possible hepatic injury and/or hemochromatosis (homozygote or heterozygote C282Y HFE mutation) > LIVER BIOPSY
- High serum titers of autoantibodies in association with other features suggestive of autoimmune liver disease (> 5 ULN aminotransferases, high globulins, or high total protein to albumin ratio) > work-up for autoimmune liver disease
- Consider presence of commonly associated comorbidities (central obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia , diabetes or insulin resistance, hypothyroidism, polycystic ovary syndrome, obstructive sleep apnea)
* NFS is based on 6 variables (age, BMI, hyperglycemia, platelet count, albumin, and AST/ALT ratio) and is calculated using the published formula http://gihep.com/calculators/hepatology/nafld-fibrosis-score/
Adapted from Chalasani N. Practice Guidance from the AASLD;Hepatology 2018;67:328-357
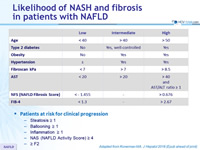
Likelihood of NASH and fibrosis in patients with NAFLD
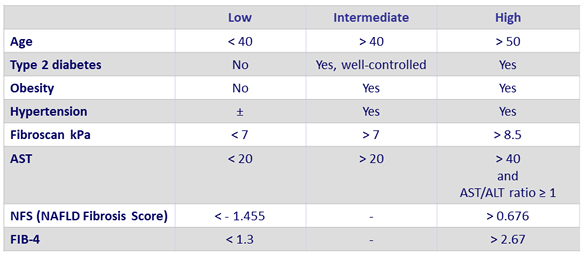
- Patients at risk for clinical progression
- Steatosis = 1
- Ballooning = 1
- Inflammation = 1
- NAS (NAFLD Activity Score) = 4
- = F2
Adapted from Konerman MA. J Hepatol 2018 (Epub ahead of print)
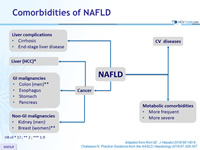
Comorbidities of NAFLD
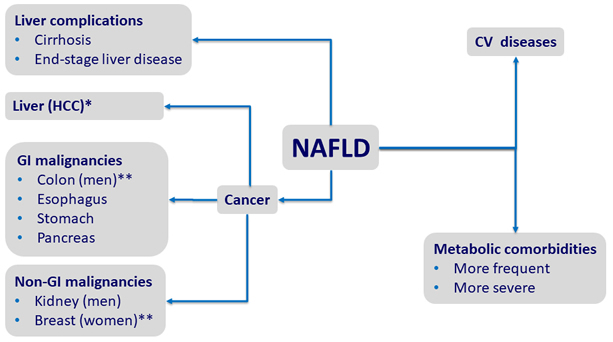
HR of
* 17 ; ** 2 ; *** 1.9
Adapted from Kim GE. J Hepatol 2018;68:140-6
;
Chalasani N. Practice Guidance from the AASLD; Hepatology 2018;67:328-357
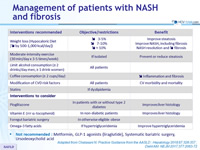
Management of patients with NASH and fibrosis
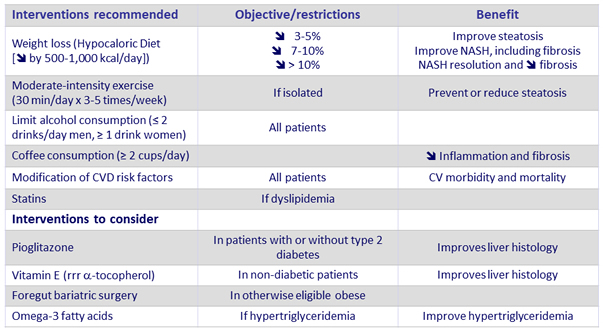
- Not recommended : Metformin, GLP-1 agonists (liraglutide), Systematic bariatric surgery, Ursodeoxycholid acid
Adapted from Chalasani N. Practice Guidance from the AASLD ; Hepatology 2018;67:328-357
;
Diehl AM. NEJM 2017;377:2063-72
Endpoints in clinical trials of NAFLD and NASH
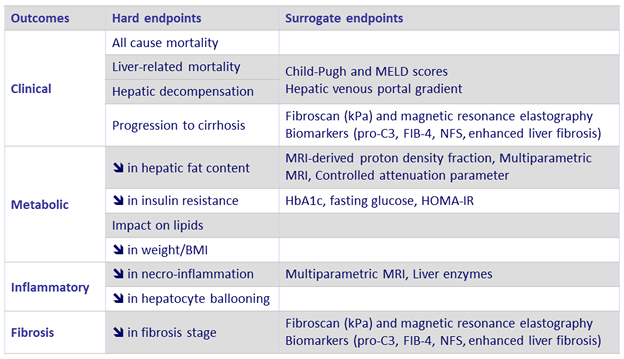
Adapted from Konerman MA. J Hepatol 2018 (Epub ahead of print)
NASH-new serum non-invasive biomarkers
- Not yet fully validated
- Could diagnose NASH and its severity
- Could identify patients likely to respond to therapy
- Chitinase-3-like protein 1(CHI3L1) – YKL-40
- Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) Test
- Comprised of TIMP-1 (tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1), PIII-NP (mino -terminal peptide of type III procollagen), and hyaluronic acid
- Pro C3
- Derived from synthesis of type III collagen
- FIB-C3 Score
- HepQuant STAT
- Quantitative liver function test 60 min after oral administration of 4 mg tetra-deuterated cholic acid
- Non-invasive score-4 (NIS4)
- Detect patients with NAS = 4 and F = 2
- Comprised of Chitinase-3-like protein 1(CHI3L1), alpha2-macroglobulin, microRNA 34a (MIR34a), and HbA1C
Adapted from Harrison SA. AASLD 2017
Current Status of Pharmacologic Treatments for NASH
- No approved therapies for NASH
- Currently available therapeutics with (some) proven efficacy
- Vitamin E
- Pioglitazone
NASH: targets for therapeutics
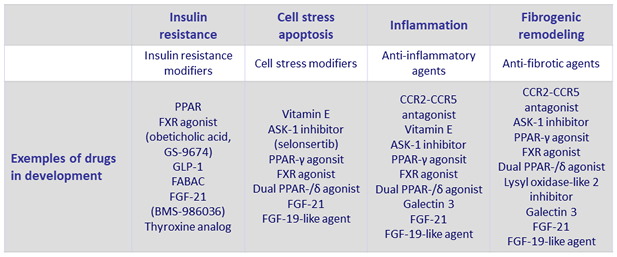
- Endpoints for clinical trials
- Disease Activity (steatohepatitis) = NAFLD Activity Score (NAS)
- Disease Progression = Fibrosis Stage
- Clinical outcomes : Cirrhosis (MELD, Portal hypertension), Liver-related outcome, death
Adapted from Konerman MA. J Hepatol 2018 (Epub ahead of print) ; Diehl AM. NEJM 2017;377:2063-72
NASH – Pharmacological agents in development
Adapted from Konerman MA. J Hepatol 2018 (Epub ahead of print)
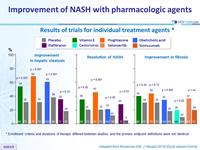
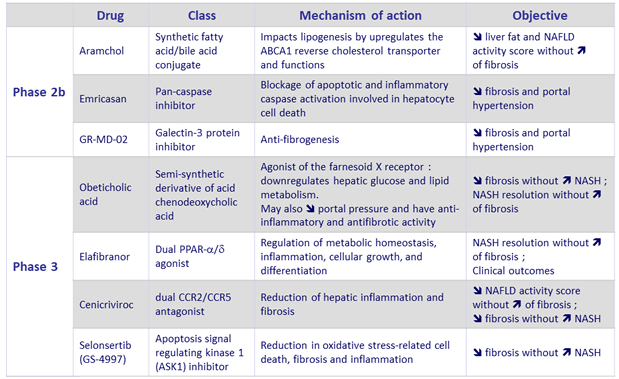
Results of trials for individual treatment agents *
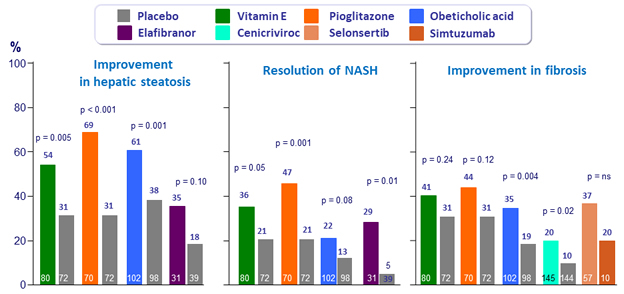
* Enrollment criteria and durations of therapy differed between studies, and the primary endpoint definitions were not identical
Adapted from Konerman MA. J Hepatol 2018 (Epub ahead of print)
NASH Combination |
 |
 |
Prevention and |