NGM282 in NASH: 3 mg vs 6 mg QD (phase 2)
Harrison SA, Lancet 2018;391:1174-85
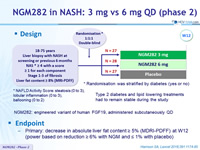
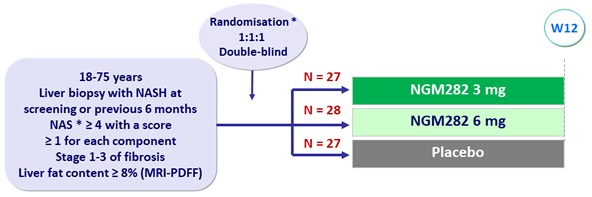
Design
Type 2 diabetes and lipid lowering treatments had to remain stable during the study
* Randomisation was stratified by diabetes (yes or no)
* NAFLD Activity Score: steatosis (0 to 3), lobular inflammation (0 to 3), ballooning (0 to 2)
- NGM282: engineered variant of human FGF19, administered subcutaneously qd
Endpoint
- Primary: decrease in absolute liver fat content = 5% (MDRI-PDFF) at W12 (power based on reduction = 6% with NGM and = 1% with placebo)
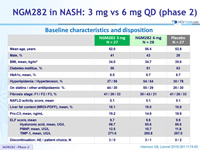
Baseline characteristics and disposition
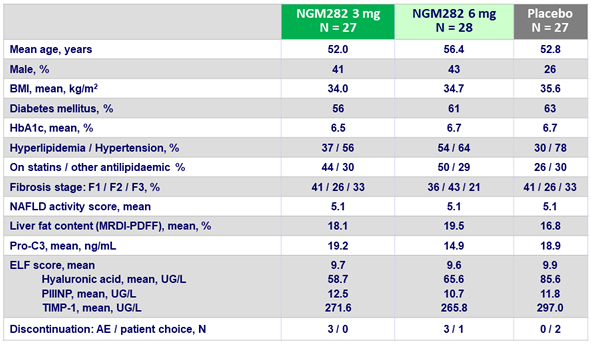
Change in liver fat content (MRDI-PDFF) at W12
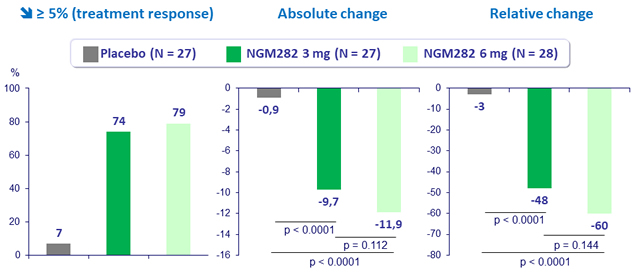
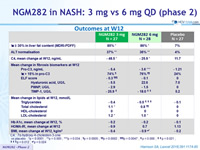
Outcomes at W12
C4 : 7a-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one
vs placebo : *p < 0.0001 ; **p = 0.005 ; ***p = 0.034 ; ¶ p = 0.0005 ; ¶¶ p = 0.0002 ; ¶¶¶ p = 0.0047 ; § p = 0.006 ; §§ p = 0.021 ;§§§ p = 0.012 ; ? p = 0.024
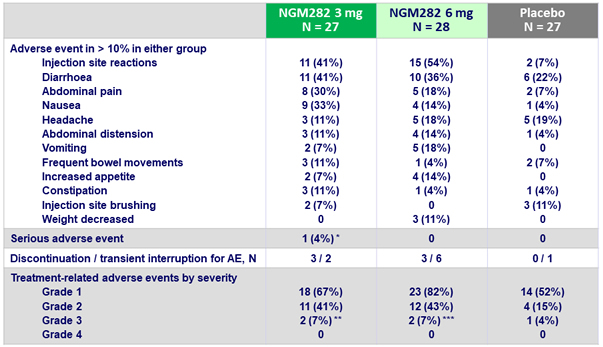
Most common adverse events
Summary
- In patients with NASH, 3 mg and 6 mg doses of NGM282 significantly and rapidly (over 12 weeks) reduced
- liver fat content, as measured by MRI-proton density fat fraction
- as well as markers of liver inflammation (ALT, AST)
- and fibrosis, as assessed by non-invasive biomarkers (pro-C3, enhanced liver fibrosis score)
- Significant decreases in serum C4 concentrations, and the ensuing increases in LDL-C were recorded with NGM282, consistent with potent target engagement and inhibition of CYP7A1
- Both doses were generally well tolerated
- In view of the similar efficacy of NGM282 3 mg and 6 mg in lowering liver fat content, doses lower than 3 mg should be evaluated to better characterise the efficacy and tolerability profile