C-EDGE TN Study: grazoprevir / elbasvir in genotype 1, 4 or 6
Grazoprevir–Elbasvir Combination Therapy for Treatment-Naïve Cirrhotic and Noncirrhotic Patients With Chronic HCV Genotype 1, 4, or 6 Infection
Zeuzem S. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:1-13
Anti-HCV
Grazoprevir
Elbasvir
Grazoprevir
Elbasvir
Genotype
1
1a
1b
1
1a
1b
Treatment history
Naive
Naive
Cirrhosis
Yes
No
Yes
No
Design
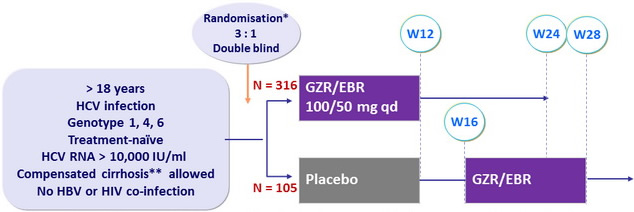
* Randomisation was stratified on genotype (1 or 4 or 6) and cirrhosis ( yes or no)
**
Metavir F4 or fibroscan > 12.5 kPa or FibroTest > 0.75 + APRI > 2
Objective
- SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU /ml) by intention to treat analysis : superiority to historical SVR12 of simeprevir + PEG-IFN + RBV (73%), at an overall 1-sided alpha value of 0.025, 99% power
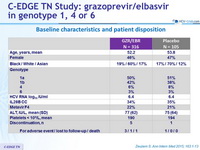
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition
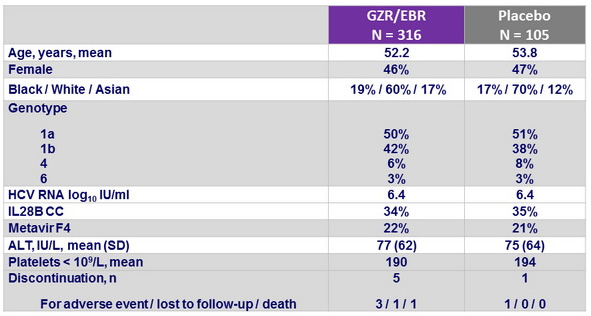
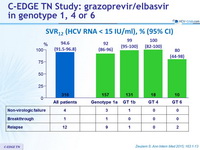
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) , % (95% CI)
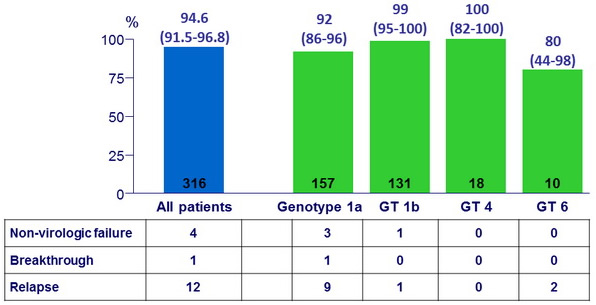
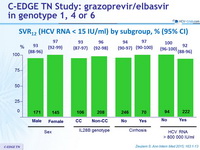
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) by subgroup , % (95% CI)
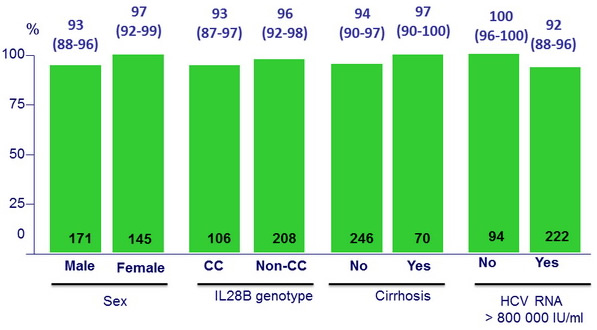
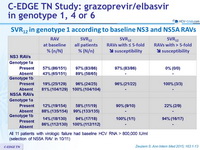
SVR12 in genotype 1 according to baseline NS3 and NS5A RAVs
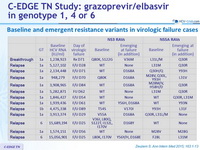
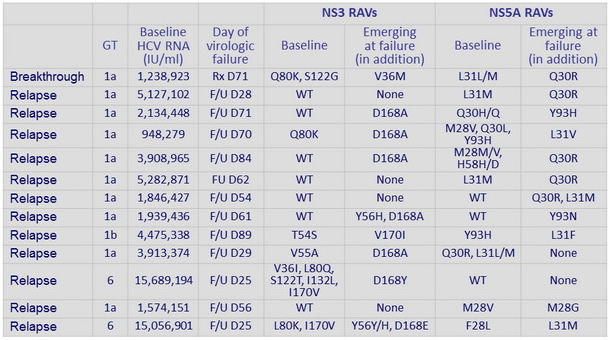
All 11 patients with virologic failure had baseline HCV RNA > 800,000 IU/ml (selection of NS5A RAV in 10/11)
Baseline and emergent resistance variants in virologic failure cases
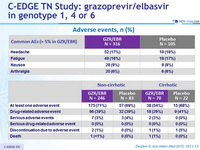
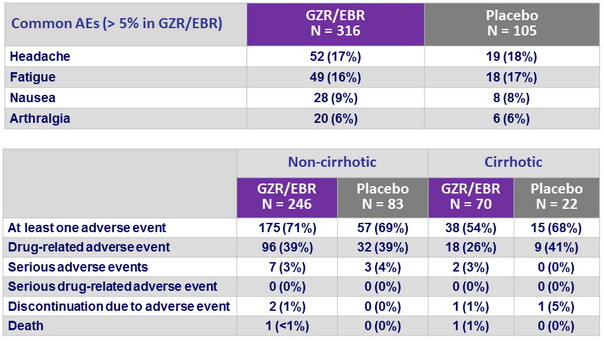
Adverse events, N (%)
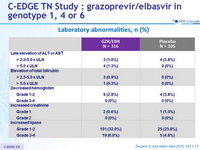
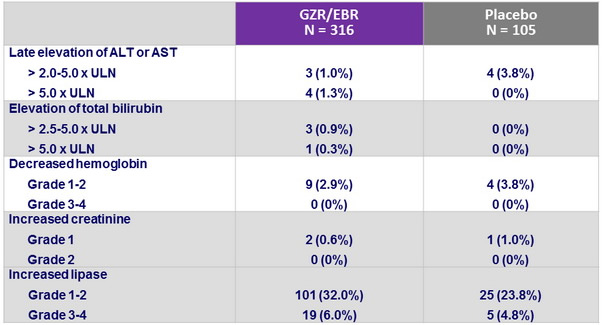
Laboratory abnormalities, n (%)
Summary
- A 12-week regimen of the oral fixed dose combination of once-daily, single-tablet of grazoprevir/elbasvir, achieved an overall SVR12 of 95%
- High efficacy in genotypes 1 and 4
- SVR12 lower in genotype 6
- High efficacy in cirrhotics (SVR12 = 97.1%)
- Lower efficacy observed among patients with high viral load (HCV RNA > 800,000 IU/ml)
- Overall virologic failure rate was 4%
- Baseline NS3 RAVS did not affect efficacy
- Association between virologic failure and the presence of baseline NS5A RAVs, which was most apparent in genotype 1a with baseline RAVs demonstrating > 5-fold potency reduction to elbasvir
- Emergence of (additional) NS3 and/or NS5A RAVs at failure was common
- Grazoprevir/elbasvir was generally well-tolerated, with a similar safety profile in cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic patients
- Limitations
- No active-control group