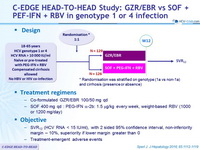
C-EDGE HEAD-TO-HEAD Study: GZR/EBR vs SOF + PEF-IFN + RBV in genotype 1 or 4 infection
Sperl J. J Hepatology 2016; 65:1112-1119
Anti-HCV
Grazoprevir
Elbasvir
Sofosbuvir
PEG-IFNα 2a
Ribavirin
Grazoprevir
Elbasvir
Sofosbuvir
PEG-IFNα 2a
Ribavirin
Genotype
1
4
1
4
Treatment history
Naive
IFN-Experienced
Naive
IFN-Experienced
Cirrhosis
Yes
No
Yes
No
Design

* Randomisation was stratified on g enotype (1a vs non-1a) and cirrhosis ( presence or absence)
Treatment regimens
- Co-formulated GZR/EBR 100/50 mg qd
- SOF 400 mg qd : PEG-IFN α-2b: 1.5 m g/kg every week, weight-based RBV (1000 or 1200 mg/day)
Objective
- SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml), with 2 sided 95% confidence interval, non-inferiority margin – 10%, superiority if lower margin greater than 0
- Treatment-emergent adverse events
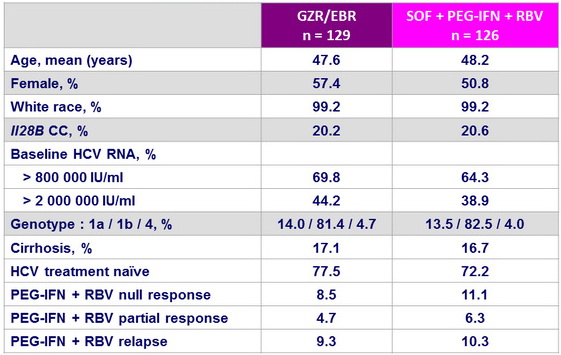
Baseline characteristics
SRV12 rates overall and by genotype
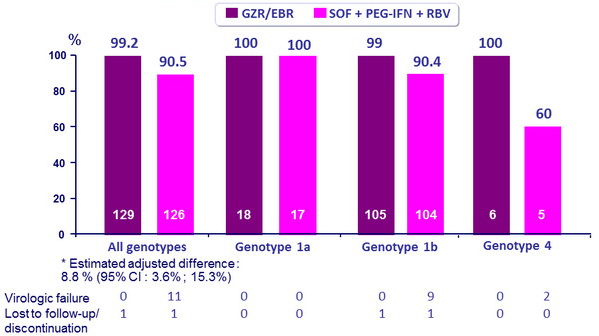
- GZR/EBR is non-inferior and superior
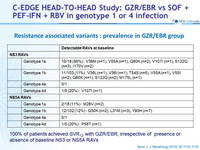
Resistance associated variants : prevalence in GZR/EBR group
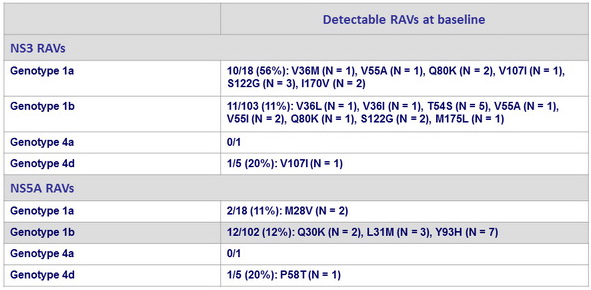
100% of patients achieved SVR12 with GZR/EBR, irrespective of presence or absence of baseline NS3 or NS5A RAVs
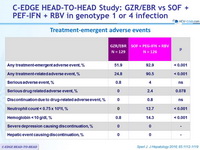
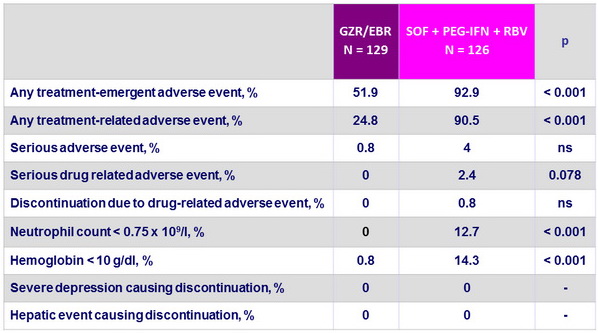
Treatment-emergent adverse events
Summary
- 12 weeks of GZR/EBR has superior efficacy to SOF + PEG-IFN
+ RBV on genotype 1 and genotype 4-infected patients
- High SVR12 in all subpopulations
- Experienced patients including PEG-IFN + RBV null responders (100%)
- Cirrhosis (100%)
- High baseline viral load (98.9 %)
- High SVR12 in all subpopulations
- Superior safety profile of GZR/EBR
- No serious drug-related adverse events
- No discontinuations due to drug-related adverse events
- Superior hematological safety profile
- No hepatic safety events