C-SCAPE Study: elbasvir ± grazoprevir ± RBV in genotypes 2, 4, 5 or 6
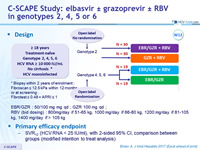
C-SCAPE Study: grazoprevir ± elbasvir ± RBV in genotypes 2, 4, 5 or 6
Brown A. J Viral Hepat 2017, Nov 20 (Epub)
Anti-HCV
Grazoprevir
Elbasvir
Ribavirin
Grazoprevir
Elbasvir
Ribavirin
Genotype
2
4
5
6
2
4
5
6
Treatment history
Naive
Naive
Cirrhosis
No
No
Design
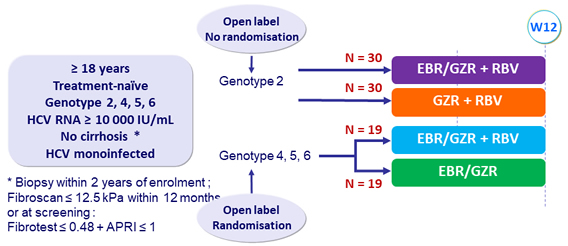
EBR/GZR : 50/100 mg mg qd ; GZR 100 mg qd ; RBV (bid dosing) : 800mg/day if 51-65 kg, 1000 mg/day if 66-80 kg, 1200 mg/day if 81 -105 kg, 1400 mg/day if > 105 kg
Primary efficacy endpoint
- SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml), with 2-sided 95% CI, comparison between groups (modified intention to treat analysis)
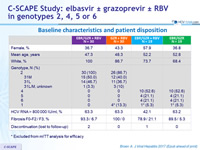
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition
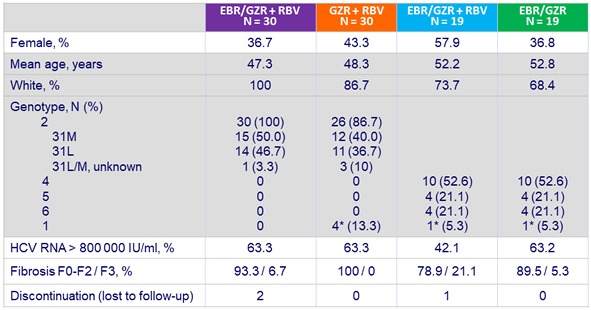
* Excluded from mITT analysis for efficacy
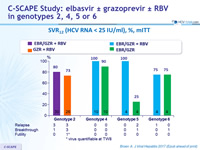
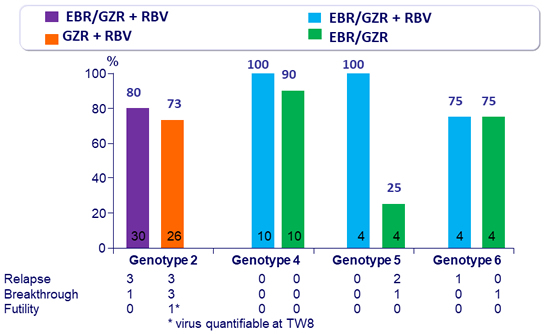
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml), %, mITT
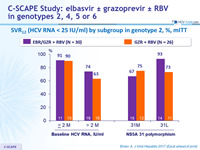
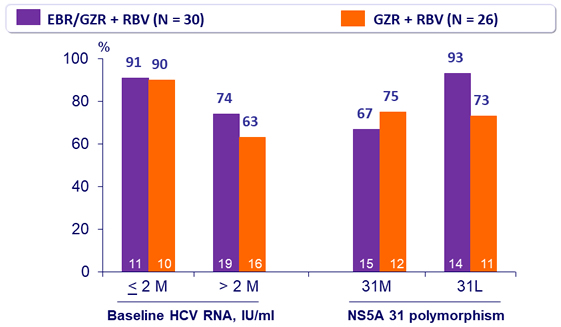
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) by subgroup in genotype 2, %, mITT
Adverse events and laboratory abnormalities, N (%)
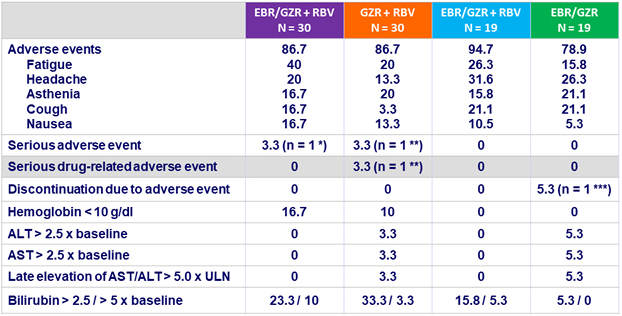
* Acute renal failure with urinary tract infection ; ** Flushing ; *** Increased AST/ATLT confounded by concurrent use of hepatotoxic drug
Summary
- In genotype 2
- 12 weeks of EBR/GZR + RBV is more efficacious than GZR + RBV, due to the added benefit of EBR in treating patients with 31L variant 12 weeks of GZR + RBV is inadequate for non-cirrhotic, treatment- naive patients with genotype 2. The triple combination is not optimal
- In genotype 4
- 12 weeks of GZR + EBR, with or without RBV, is highly efficacious for non-cirrhotic, treatment-naive patients
- In genotype 5
- 12 weeks of GZR + EBR + RBV appears to be more effective than GZR + EBR
- In genotype 6
- 12 weeks regimen of GZR + EBR ± RBV is moderately effective (SVR 12 of 75%) for non-cirrhotic, treatment-naive patients
- Safety
- 1 case of discontinuation for adverse event (1%)