COMMAND-3 Study: DCV vs TVR, in combination with PEG-IFN + RBV, for genotype 1a or 1b
Jacobson I. World J Gastroenterol 2016;22:3418-31
Anti-HCV
Daclatasvir
PEG-IFNα 2a
Ribavirin
Daclatasvir
PEG-IFNα 2a
Ribavirin
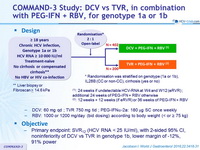
Genotype
1a
1b
1a
1b
Treatment history
Naive
Naive
Cirrhosis
No
No
Design
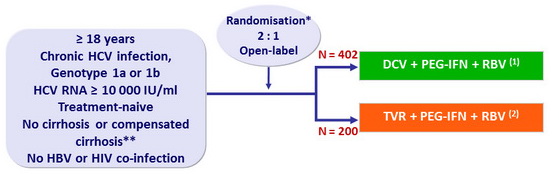
* Randomisation was stratified on genotype (1a or 1b), IL28B (CC or non-CC), cirrhosis (yes or no)
** Liver biopsy or Fibroscan > 14.6 kPa
(1) : 24 weeks if undetectable HCV-RNA at W4 and W12 ( eRVR ) ; additional 24 weeks of PEG-IFN + RBV otherwise
(2) : 12 weeks + 12 weeks (if eRVR ) or 36 weeks of PEG-IFN + RBV
- DCV: 60 mg qd ; TVR 750 mg tid ; PEG-IFNα-2a: 180 µg SC once weekly
- RBV: 1000 or 1200 mg/day (bid dosing) according to body weight (< or ≥ 75 kg)
Objective
- Primary endpoint: SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU /ml) , with 2-sided 95% CI, noninferiority of DCV vs TVR in genotype 1b, lower margin of -12%, 91% power
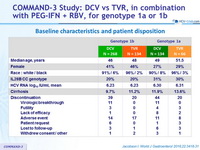
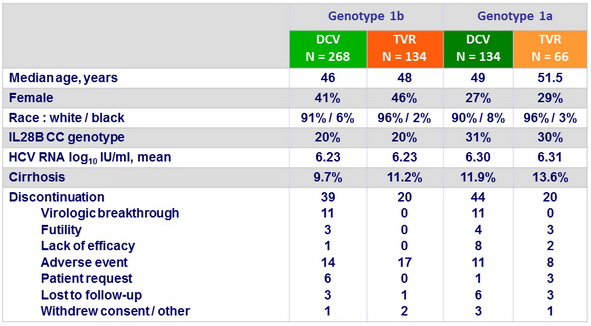
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition
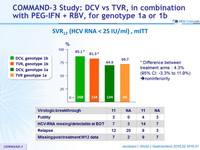
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml), mITT
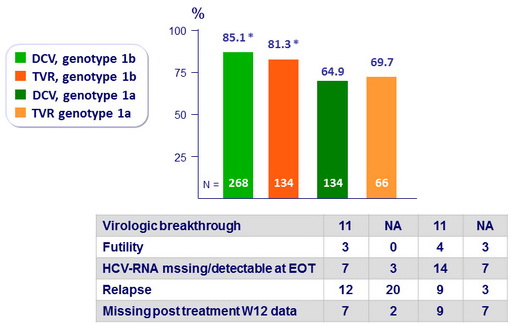
-
Difference between treatment arms : 4.3% (95% CI: -3.3% to 11.9%) » noninferiority
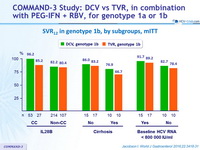
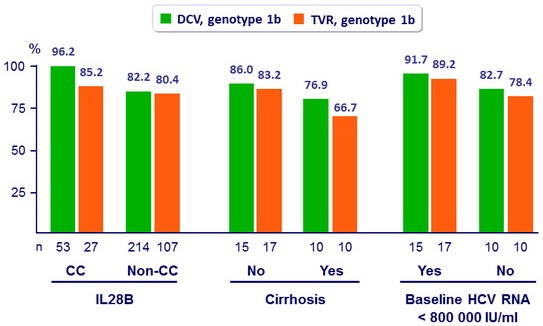
SVR12 in genotype 1b, by subgroups, mITT
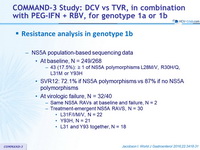
Resistance analysis in genotype 1b
- NS5A population-based sequencing data
- At baseline, N = 249/268
- 43 (17.5%): = 1 of NS5A polymorphisms L28M/V, R30H/Q, L31M or Y93H
- SVR12: 72.1% if NS5A polymorphisms vs 87% if no NS5A polymorphisms
- At virologic failure, N = 32/40
- Same NS5A RAVs at baseline and failure, N = 2
- Treatment-emergent NS5A RAVS, N = 30
- L31F/I/M/V, N = 22
- Y93H, N = 21
- L31 and Y93 together, N = 18
- At baseline, N = 249/268
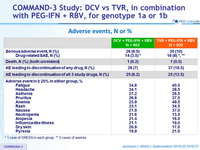
Adverse events, N or %
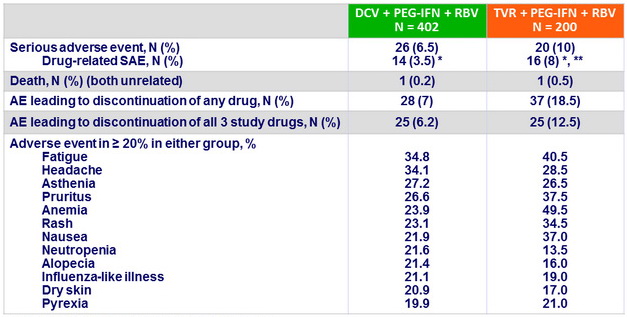
* 1 case of DRESS in each group, ** 5 cases of anemia
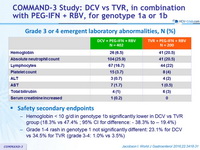
Grade 3 or 4 emergent laboratory abnormalities, N (%)
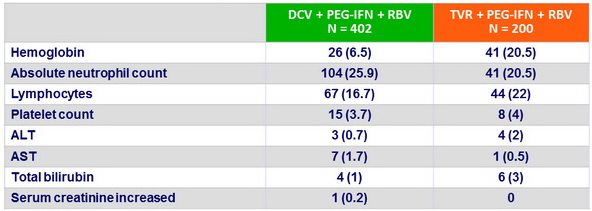
Safety secondary endpoints
- Hemoglobin < 10 g/dl in genotype 1b significantly lower in DCV vs TVR group (18.3% vs 47.4% ; 95% CI for difference: - 38.3% to – 19.4%)
- Grade 1-4 rash in genotype 1 not significantly different: 23.1% for DCV vs 34.5% for TVR (grade 3-4: 1.0% vs 3.5%)
Summary
- This head-to-head comparison of two classes of DAAs in treatment naive genotype 1b infected patients demonstrates that DCV + PEG-IFN + RBV is noninferior to TVR + PEG-IFN + RBV for SVR12
- High SVR12 was achieved in genotype 1b infected patients across all subgroups of baseline factors known to affect response rates to PEG-IFN + RBV
(cirrhosis, IL28B genotype, age, sex, baseline viral load)
- In difficult-to-cure patients with cirrhosis, SVR12 was higher with DCV + PEG-IFN + RBV than with TVR+ PEG-IFN + RBV (76.9% vs 66.7%)
- Post treatment relapse was more frequent with TVR than with DCV (15% vs 5%), for genotype 1b
- SVR 12 with DCV + PEG-IFN + RBV was lower and virologic failure was more frequent in patients infected with genotype 1a
- Lower resistance barrier of DCV in genotype 1a ?
- DCV + PEG-IFN + RBV was generally well tolerated, with a significantly lower rate of anemia, and an observed lower rate of rash-related events compared with TVR+ PEG-IFN + RBV