C-WORTHY Study: grazoprevir + elbasvir ± ribavirin for genotype 1
Efficacy and safety of 8 weeks versus 12 weeks of treatment with grazoprevir (MK-5172) and elbasvir (MK-8742) with or without ribavirin in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 mono-infection and HIV/hepatitis C virus co-infection (C-WORTHY): a randomised, open-label phase 2 trial
Sulkowski M. Lancet 2015;385:1087-97
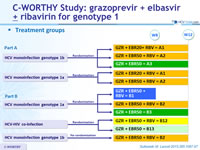
Anti-HCV
Grazoprevir
Elbasvir
Ribavirin
Grazoprevir
Elbasvir
Ribavirin
Genotype
1b
1b
Treatment history
Naive
Naive
Cirrhosis
No
No
Special population
HIV co-infection
HIV co-infection
Design
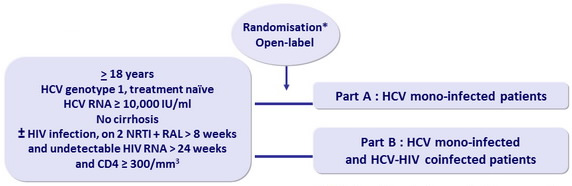
* Patients and investigators masked to group assignment
Dosage of study drugs
- Grazoprevir (GZR) 100 mg qd
- Elbasvir (EBR) : 20 or 50 mg qd
- RBV (bid dosing) : 800 mg/day if 51-65 kg, 1000 mg/day if 66-80 kg, 1200 mg/day if 81-105 kg, 1400 mg/day if > 105 kg
Primary efficacy endpoint
- SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml), with 2-sided 95% CI, comparison between groups
Treatment groups
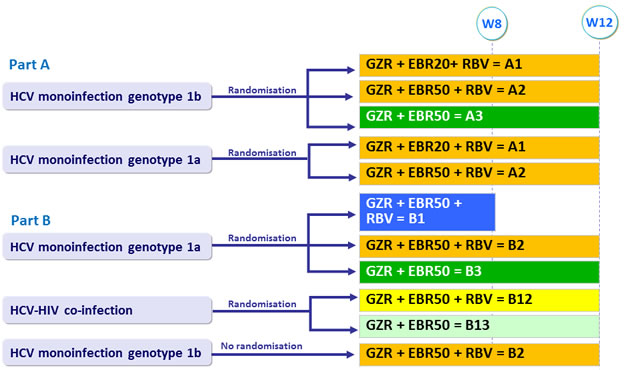
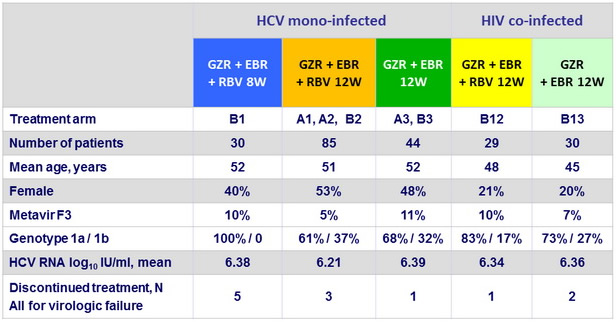
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition
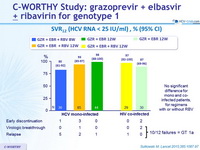
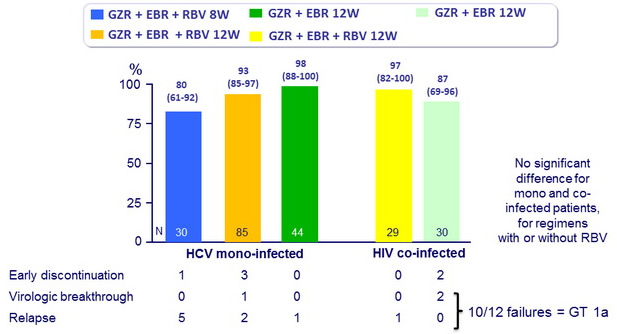
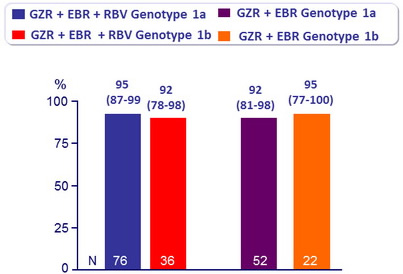
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml), % (95% CI)
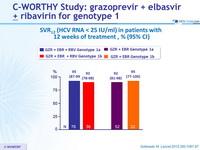
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml) in patients with 12 weeks of treatment, % (95% CI)
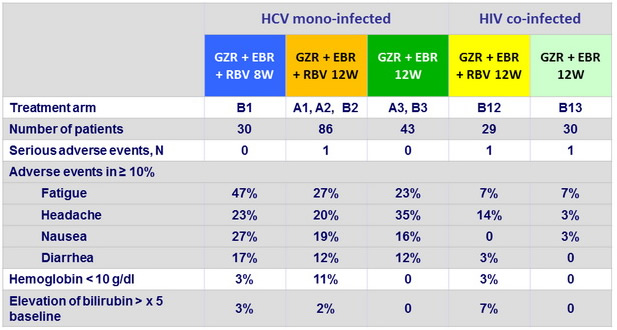
Adverse events and laboratory abnormalities
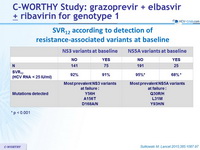
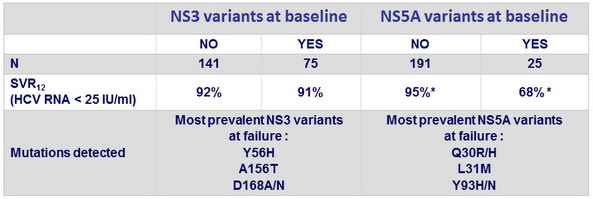
SVR12 according to detection of resistance-associated variants at baseline
* p < 0.001
Summary
- In this phase II study, 12 weeks of oral treatment with grazoprevir and elbasvir, with or without RBV, was well tolerated and led to high rates of SVR12 (87-98%) in previously untreated patients without cirrhosis with HCV genotype 1 monoinfection or HIV/HCV co-infection
- The addition of RBV was not associated with increased rates of SVR12
- Similar efficacy was seen in patients with genotype 1a and 1b
- SVR12 was similar with 12 weeks of treatment in mono and co-infected patients
- 8 weeks of GZR + EBR + RBV led to suboptimal SVR12 , mainly because of relapse
- Patients with NS5A baseline resistance-associated variants had lower SVR12
- Virological relapse was associated with emergence of resistance-associated variants to one or both of the drugs (GZR, EBR) in the regimen
- Treatment-emergent, clinically significant, adverse events were infrequent
- No discontinuation for adverse event In HIV co-infected patients, adverse events were less frequently reported, and HIV suppression was maintained