ION-1 Study: LDV/SOF ± RBV for genotype 1
Ledipasvir and Sofosbuvir for Untreated HCV Genotype 1 Infection
Afdhal N. NEJM 2014; 370:1889-98
Anti-HCV
Ledipasvir
Sofosbuvir
Ribavirin
Ledipasvir
Sofosbuvir
Ribavirin
Genotype
1
1a
1b
1
1a
1b
Treatment history
Naive
Naive
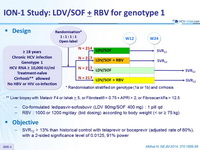
Design
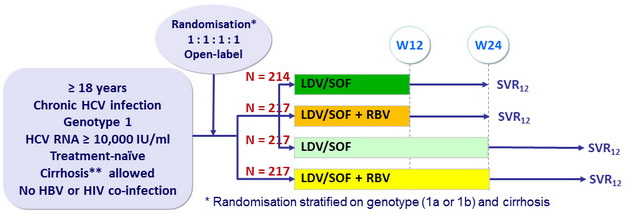
*
Randomisation stratified on genotype (1a or 1b) and cirrhosis
- Co-formulated ledipasvir-sofosbuvir (LDV 90mg/SOF 400 mg) : 1 pill qd
- RBV : 1000 or 1200 mg/ day ( bid dosing ) according to body weight (< or = 75 kg)
Objective
- SVR12 > 13% than historical control with telaprevir or boceprevir (adjusted rate of 60%), with a 2-sided significance level of 0.0125, 91% power
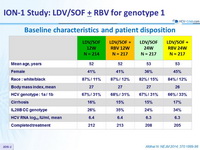
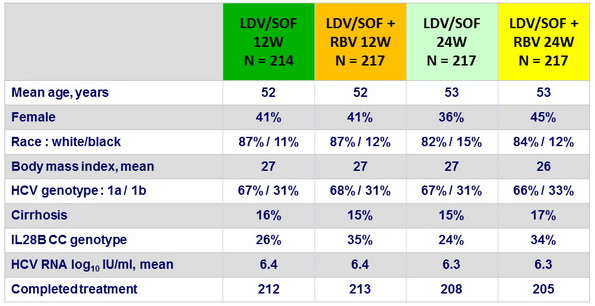
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition
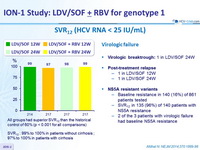
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ mL)
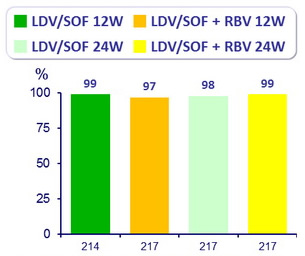
All groups had superior SVR12 than the historical control of 60% (p < 0.001 for all comparisons)
SVR12 : 99% to 100% in patients without cirrhosis ; 97% to 100% in patients with cirrhosis
Virologic failure
- Virologic breaktrough : 1 in LDV/SOF 24W
- Post-treatment relapse
- 1 in LDV/SOF 12W
- 1 in LDV/SOF 24W
- NS5A resistant variants
- Baseline resistance in 140 (16%) of 861 patients tested
- SVR12 in 135 (96%) of 140 patients with NS5A resistance
- 2 of the 3 patients with virologic failure had baseline NS5A resistance
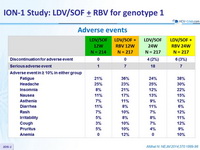
Adverse events
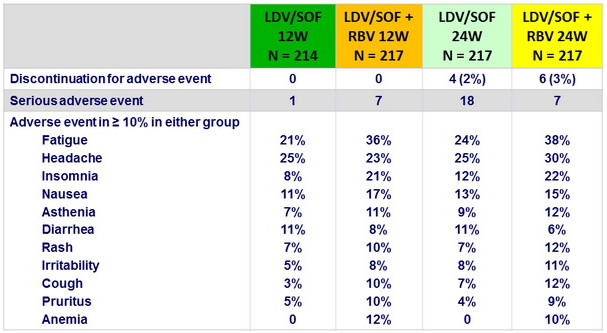
Summary
- 12 weeks of the single-tablet regimen of LDV/SOF was a highly effective treatment for a broad range of patients with HCV genotype 1 infection who had not been treated previously
- No additional benefit appeared to be associated with the addition of RBV or with extension of the duration of treatment to 24 weeks
- addition of RBV increased toxicity without providing additional efficacy
- Safety of LDV/SOF was similar to the one previously reported with SOF alone
- Virologic failure was extremely rare in this study population, occurring in only 0.3% of patients (3 of 865)
- The 2 patients with relapse had no evidence of mutations conferring resistance to SOF
- Both patients had mutations associated with resistance to NS5A inhibitors both at baseline and at the time of relapse