QUEST-1 Study: SMV + PEG-IFN + RBV for genotype 1
Simeprevir with pegylated interferon alfa 2a plus ribavirin in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection (QUEST-1): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Jacobson IM. Lancet 2014;384:403-13
Anti-HCV
Simeprevir
PEG-IFNα 2a
Ribavirin
Simeprevir
PEG-IFNα 2a
Ribavirin
Genotype
1
1
Treatment history
Naive
Naive
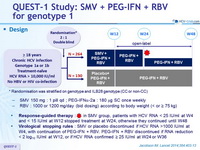
Design
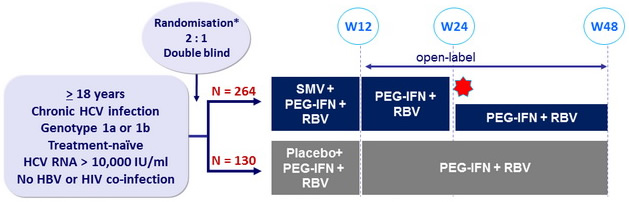
* Randomisation was stratified on genotype and ILB28 genotype (CC or non-CC)
Treatment regimens
- SMV 150 mg : 1 pill qd ; PEG-IFNα-2a : 180 mg SC once weekly
- RBV : 1000 or 1200 mg/day (bid dosing) according to body weight (< or ≥ 75 kg)
Response-guided therapy : in SMV group, patients with HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml at W4 and < 15 IU/ml at W12 stopped treatment at W24, otherwise they continued until W48
Virological stopping rules : SMV or placebo discontinued if HCV RNA >1000 IU/ml at W4, with continuation of PEG-IFN + RBV. PEG-IFN + RBV discontinued if RNA reduction < 2 log 10 IU/ml at W12, or if HCV RNA confirmed = 25 IU/ml at W24 or W36
Objectives
- Difference in SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml) between the 2 groups : estimation of 45% in the control group, power of 90% to detect a difference > 20%, by intention to treat
- Sensitivity analysis : comparison of SVR12 in both groups with a logistic regression model including baseline HCV RNA (log10 IU/ml, included as a continuous variable) and the stratification factors (HCV genotype 1 subtype and IL28B genotype)
- Secondary endpoints : SVR24 , % patients stopping treatment at W24 based on response-guided therapy, failure, safety
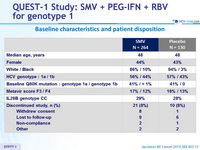
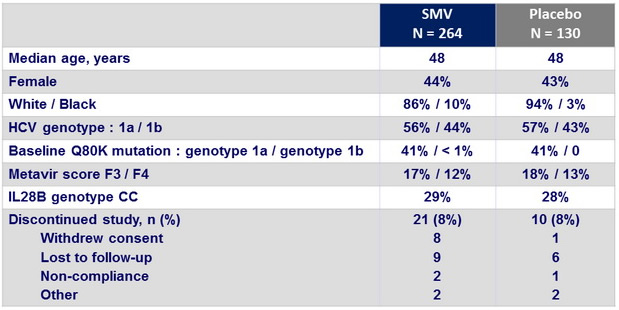
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition
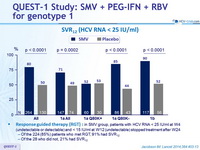
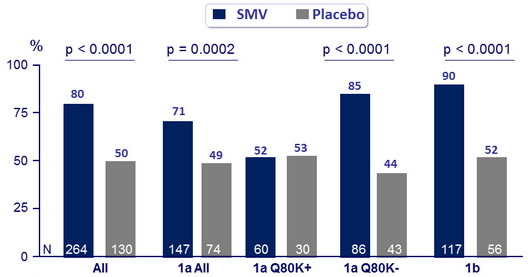
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU /ml)
Response-guided therapy : in SMV group, patients with HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml at W4 (undetectable or detectable) and < 15 IU/ml at W12 (undetectable) stopped treatment after W24
- Of the 224 (85%) patients who met RGT, 91% had SVR12
- Of the 28 who did not, 21% had SVR12
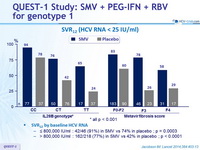
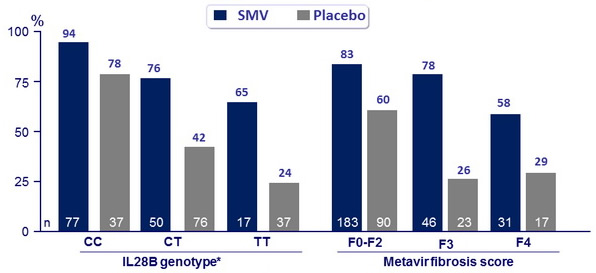
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU /ml)
SVR12 by baseline HCV RNA :
- ≤ 800,000 IU/ml : 42/46 (91%) in SMV vs 74% in placebo ; p = 0.0003
- > 800,000 IU/ml : 162/218 (77%) in SMV vs 42% in placebo ; p < 0.0001
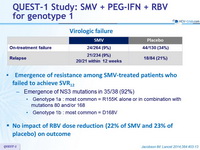
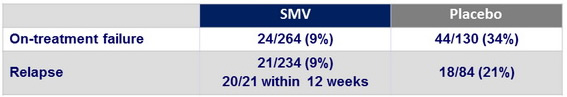
Virologic failure
- Emergence of resistance among SMV-treated patients who failed to achieve SVR12
- Emergence of NS3 mutations in 35/38 (92%)
- Genotype 1a : most common = R155K alone or in combination with mutations 80 and/or 168
- Genotype 1b : most common = D168V
- Emergence of NS3 mutations in 35/38 (92%)
- No impact of RBV dose reduction (22% of SMV and 23% of placebo) on outcome
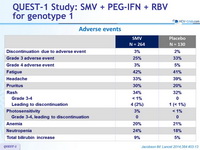
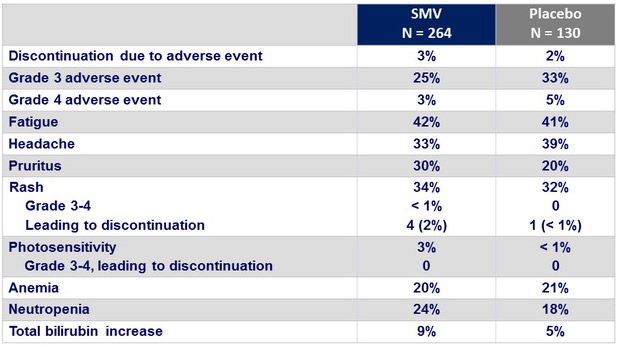
Adverse events
Summary
- A significantly higher percentage of treatment-naive patients with chronic HCV genotype 1 infection achieved SVR12 (primary efficacy endpoint) with SMV in combination with PEG-IFN + RBV than with placebo in combination with PEG-IFN + RBV and has lower on-treatment failure and relapse rates.
- 85% of patients in the SMV group met criteria for response-guided therapy and were eligible to shorten treatment and stop at W24, and 91% of these subsequently achieved SVR12
- HCV genotype 1a, IL28B non-CC genotype, cirrhosis, and high baseline HCV RNA were associated with lower SVR rates
- In patients with HCV genotype 1a who had the Q80K polymorphism at baseline, SVR12 was significantly lower, and not different between SMV and placebo
- Most patients treated with SMV who did not achieve SVR12 had emergent mutations at the time of failure
- The reported adverse events in the SMV group were clinically manageable, and most were grade 1 or 2. A lower percentage of patients in the SMV group discontinued treatment than did those in the placebo group