ASPIRE Study: SMV + PEG-IFN + RBV for genotype 1 experienced patients
Simeprevir Increases Rate of Sustained Virologic Response Among Treatment-Experienced Patients With HCV Genotype-1 Infection: A Phase IIb Trial
Zeuzem S. Gastroenterology 2014;146:430-41
Anti-HCV
Simeprevir
Simeprevir
Genotype
1
1a
1b
1
1a
1b
Treatment history
Naive
IFN-Experienced
Naive
IFN-Experienced
Cirrhosis
Yes
No
Yes
No
Special population
HIV co-infection
HIV co-infection
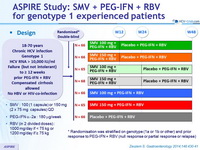
Design
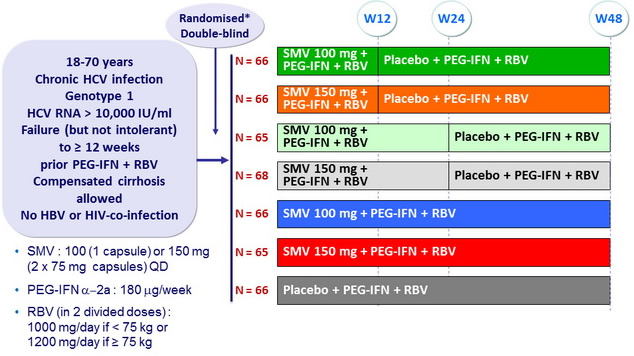
* Randomisation was stratified on genotype (1a or 1b or other) and prior response to PEG-IFN + RBV (null response or partial response or relapse)
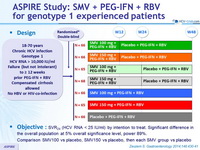
Objective
- SVR 24 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml) by intention to treat. Significant difference in the overall population at 5% o verall significance level, power 89%
- Comparison SMV100 vs placebo, SMV150 vs placebo, then each SMV group vs placebo
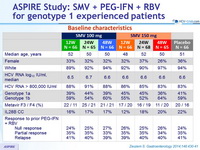
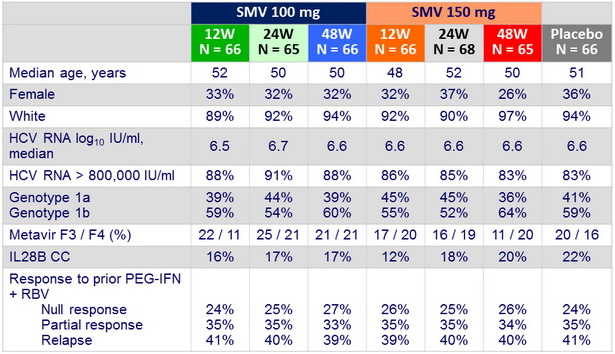
Baseline characteristics
Protocol-defined virologic stopping rules
- Patients with an insufficient response to treatment, ie, not achieving 1 log 10 reduction from baseline in HCV RNA at W 4, 2 log 10 reduction from baseline in HCV RNA at W 12, or HCV RNA = 25 IU/ml detectable at W 24 or W36, discontinued all study medication (SMV/placebo and PEG-IFN/RBV)
- Study medication was also discontinued if viral breakthrough (confirmed, on treatment increase in HCV RNA of > 1 log 10 IU/ml from the lowest level reached, or confirmed HCV RNA > 100 IU/ml in patients with HCV RNA previously < lower limit of quantification of 25 IU/ml or undetectable) at any time point during treatment
Premature discontinuation
- N = 39 (8,4%) : withdrawal of consent, N = 21, lost to follow-up, N = 12, adverse event, N = 1, other, N = 5
Discontinuation of study medication
- SMV/placebo + PEG-IFN + RBV, N = 134 (29%)
- SMV/placebo only, N = 7 (1,5%)
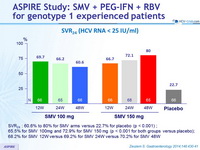
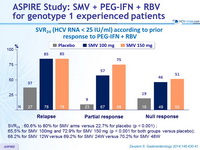
SVR 24 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml)
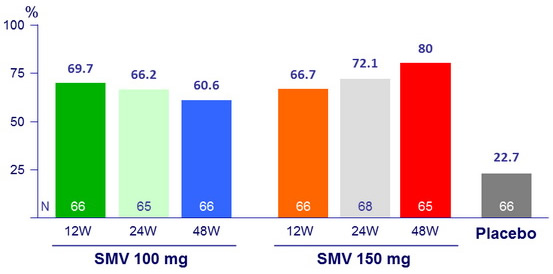
- SVR 24 : 60.6% to 80% for SMV arms versus 22.7% for placebo (p < 0.001) ;
- 65.5% for SMV 100mg and 72.9% for SMV 150 mg (p < 0.001 for both groups versus placebo);
- 68.2% for SMV 12W versus 69.2% for SMV 24W versus 70.2% for SMV 48W
SVR 24 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml) according to prior response to PEG-IFN + RBV
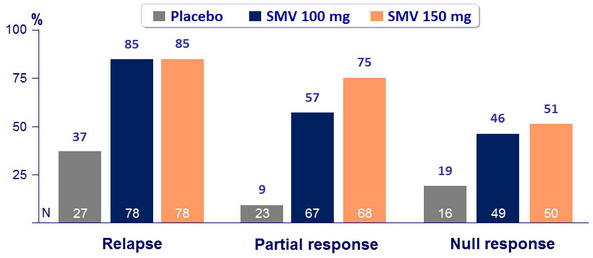
- SVR 24 : 60.6% to 80% for SMV arms versus 22.7% for placebo (p < 0.001) ;
- 65.5% for SMV 100mg and 72.9% for SMV 150 mg (p < 0.001 for both groups versus placebo);
- 68.2% for SMV 12W versus 69.2% for SMV 24W versus 70.2% for SMV 48W
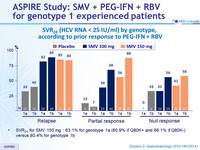
SVR 24 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml) by genotype, according to prior response to PEG-IFN + RBV
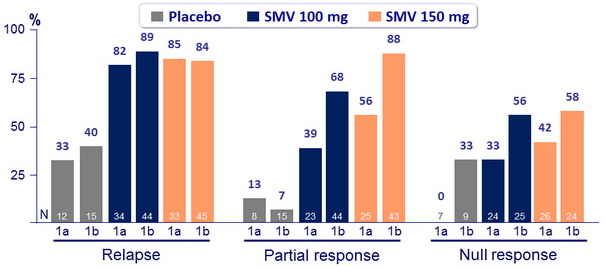
- SVR 24 for SMV 150 mg : 63.1% for genotype 1a (60.9% if Q80K+ and 66.1% if Q80K-) versus 80.4% for genotype 1b
SVR 24 in SMV 150 mg group according to other characteristics and prior response to PEG-IFN + RBV
- Metavir F4
- Relapse : 73%
- Prior partial response : 82%
- Prior null response : 31%
- IL28B genotype
- CC : 88%
- CT : 74%
- TT : 61%
Treatment failure
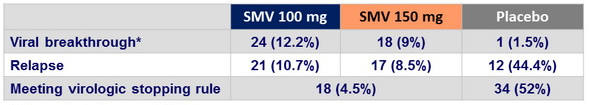
* Generally before or at W12
NS3 emerging mutations
- Viral breakthrough : 41/42
- Relapse : 34/35
- Mostly R155K or D168V alone or a combination of Q80K or Q80R, R155K, and/or D168E mutations
- Genotype 1a : mainly R155K ; genotype 1b : mainly D168V
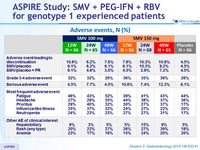
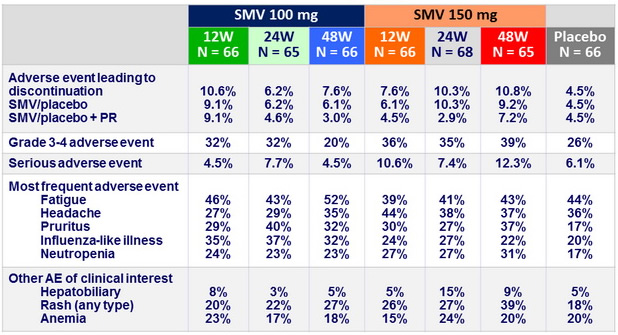
Adverse events, N (%)
Summary
- Simeprevir once daily in combination with PEG-IFN + RBV achieved significantly improved SVR rates compared with placebo plus PEG-IFN + RBV in patients infected with HCV genotype 1 who failed to respond to previous PEG- IFN + RBV therapy
- Higher SVR 24 rates were seen in patients with a prior partial or null response treated with SMV150 mg compared with SMV 100 mg. This trend was also observed across most subgroups
- No consistent beneficial trend for treatment duration > 12W with SMV
- SVR 24 with SMV 150 mg was higher in genotype 1b than 1a among patients with a prior null or partial response
- SVR 24 in patients with cirrhosis in the SMV150 mg group were substantially higher than in the placebo group (62% versus 0%, respectively)
- Viral breakthrough and relapse tended to be less common with SMV 150 mg versus 100 mg. Almost all failures had emerging NS3 resistance mutations
- No difference in incidence or severity of adverse events with SMV vs placebo
- No increase in anemia. Rash and neutropenia were more common with SMV
- Transient mild hyperbilirubinemia with SMV (inhibition of OATP1B1)