C-SALT Study: grazoprevir + elbasvir in genotype 1 with Child-Pugh B cirrhosis
Efficacy and Safety of Grazoprevir and Elbasvir in Hepatitis C Genotype 1–infected Patients with Child-Pugh Class B Cirrhosis (C-SALT PART A)
Jacobson IM. EASL 2015, Abs. O008
Anti-HCV
Grazoprevir
Elbasvir
Grazoprevir
Elbasvir
Genotype
1a
1a
Treatment history
IFN-Experienced
IFN-Experienced
Cirrhosis
Yes
Yes
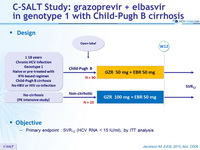
Design
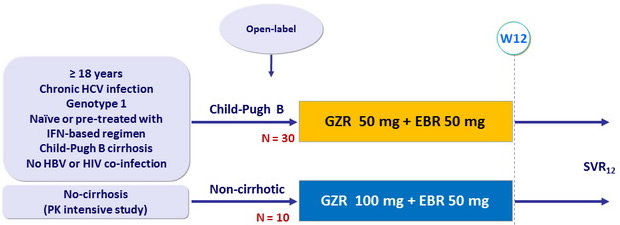
Objective
-
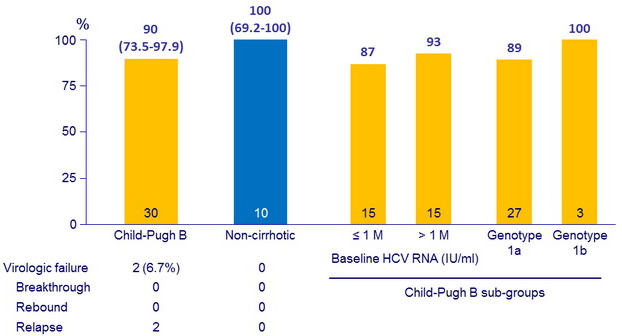
Primary endpoint : SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU /ml) , by ITT analysis
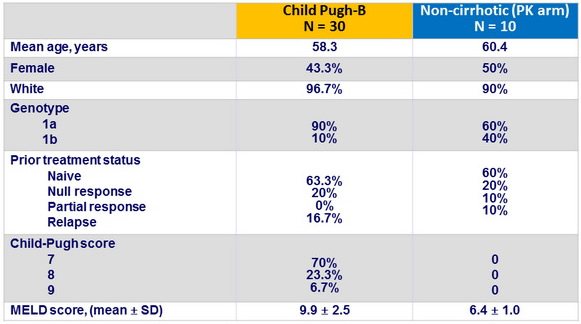
Baseline characteristics
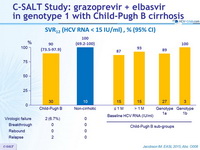
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) , % (95% CI)
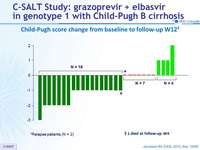
Child-Pugh score change from baseline to follow-up W12 §
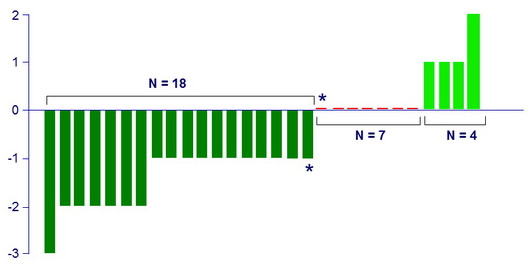
*Relapse patients (N = 2)
§ 1 died at follow-up W4
Pharmacokinetics
- Plasma samples collected over 24 hours at treatment W4
- PK group (non-cirrhotic, N = 9) with GZR 100 mg
- Child-Pugh B (N = 9) with GZR 50 mg
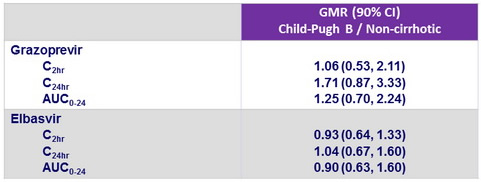
- GZR exposure was slightly higher (not significant) in patients with Child-Pugh B cirrhosis receiving 50 mg dose compared to non-cirrhotic patients receiving
100 mg dose - EBR (50 mg) PK was similar in both patient populations
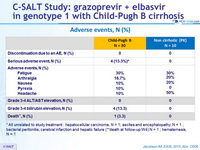
Adverse events, N (%)

* All unrelated to study treatment : hepatocellular carcinoma, N = 1; ascites and encephalopathy, N = 1 ; bacterial peritonitis, cerebral infarction and hepatic failure (**death at follow-up W4) N = 1 ; hematemesis, N = 1
Summary
- High rates of virologic response were observed in Child-Pugh B patients receiving a combination of once-daily GZR 50 mg + EBR 50 mg
- The regimen was well tolerated with no evidence of hepatotoxicity
- Plasma GZR exposure was slightly higher in Child-Pugh B patients receiving 50 mg compared to non-cirrhotic patients receiving 100 mg
- EBR exposure was similar in both Child-Pugh B and non-cirrhotic groups
- This regimen was highly effective and well-tolerated in a traditionally hard-to-treat patient group with no currently approved treatment options