ATTAIN Study: simeprevir versus telaprevir, with PEG-IFN + RBV in previous non responders with genotype 1
Simeprevir versus telaprevir with peginterferon and ribavirin in previous null or partial responders with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection (ATTAIN): a randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority phase 3 trial
Reddy KR. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15:27-35
Anti-HCV
Simeprevir
PEG-IFNα 2a
Ribavirin
Simeprevir
PEG-IFNα 2a
Ribavirin
Genotype
1
1a
1b
1
1a
1b
Treatment history
IFN-Experienced
IFN-Experienced
Cirrhosis
Yes
No
Yes
No
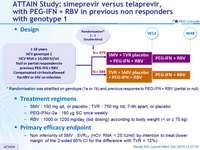
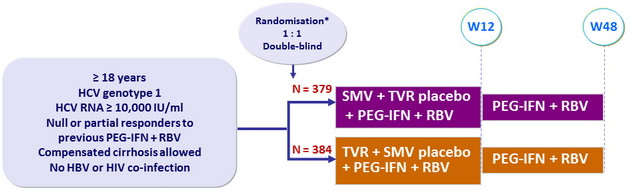
Design
*
Randomisation was stratified on genotype (1a or 1b) and previous response to PEG-IFN + RBV (partial or null)
Treatment regimens
- SMV : 150 mg qd , or placebo ; TVR : 750 mg tid , 7-9h apart, or placebo
- PEG-IFNα-2a : 180 m g SC once weekly
- RBV : 1000 or 1200 mg/day (bid dosing) according to body weight (< or = 75 kg)
Primary efficacy endpoint
- Non inferiority of SMV : SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU /ml) by intention to treat (lower margin of the 2-sided 95% CI for the difference with TVR = 12%)
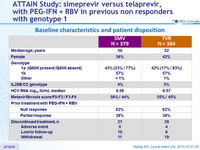
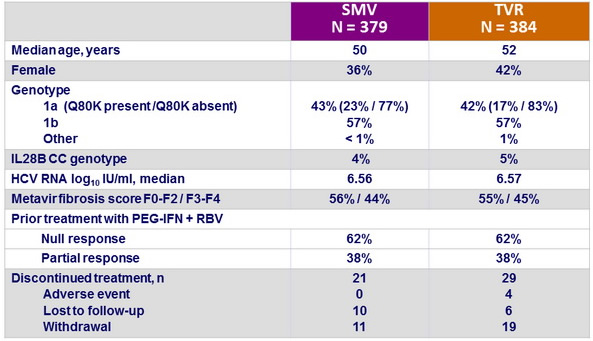
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition
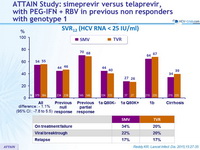
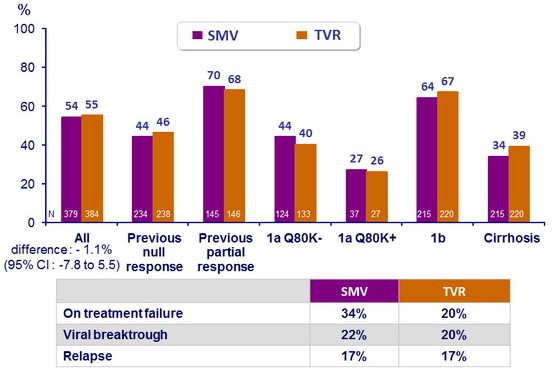
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU /ml)
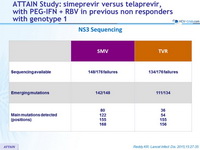
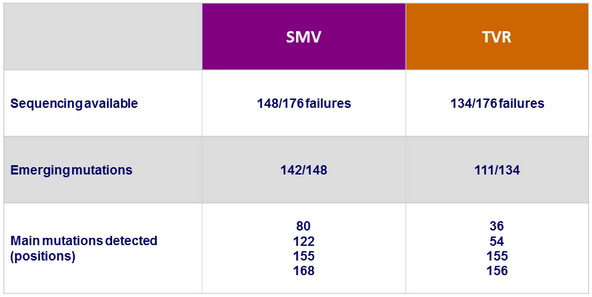
NS3 Sequencing
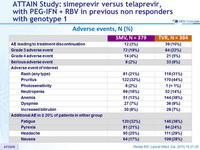
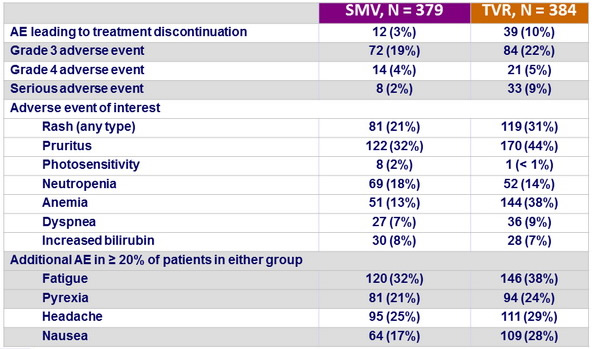
Adverse events, N (%)
Summary
- SMV + PEG-IFN + RBV showed non-inferiority with regard to SVR12 to TVR + PEG-IFN + RBV in patients with chronic HCV genotype 1 infection and compensated liver disease who were null or partial responders to previous treatment with PEG-IFN + RBV
- Non-inferiority was met for null or partial responders separately as well
- Rates of on-treatment failure, viral breakthrough, and relapse were similar between the two treatment groups
- The incidence of adverse events deemed at least possibly related to SMV or TVR was noticeably lower in the SMV group, and most adverse events were grade 1 or 2
- Serious adverse events were infrequent and less common in the SMV group, and fewer patients needed to discontinue SMV compared with TVR because of an adverse event