PEARL-I Study – Part 2 : ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir ± ribavirin for HCV genotype 1b
Efficacy and Safety of Ombitasvir, Paritaprevir, and Ritonavir in an Open-label Study of Patients With Genotype 1b Chronic Hepatitis C Virus, With and Without Cirrhosis
Lawitz E. Gastroenterology 2015; 149: 971-80
Anti-HCV
Ombitasvir
Paritaprevir/ritonavir
Ombitasvir
Paritaprevir/ritonavir
Genotype
1b
1b
Treatment history
Naive
IFN-Experienced
Naive
IFN-Experienced
Cirrhosis
Yes
No
Yes
No
Design
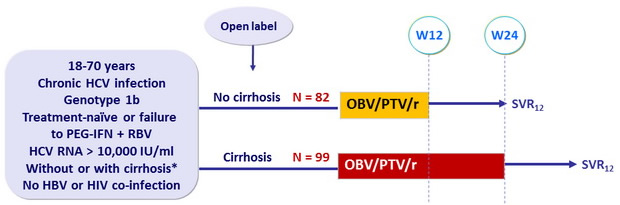
* Metavir F4 or Ishak > 4 or F ibroscan > 14 .6 kPa or FibroTest, Child score = 6
Treatment regimen
- Co-formulated ombitasvir (OBV)/ paritaprevir (PTV)/ rironavir (r) : 25/150/100 mg QD = 2 tablets
Objective
- SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml) with 95% CI : hypothesis of a 25% difference between treatment-naïve (95%) and prior null-responders without cirrhosis (70%), 80% power with two-sided significance level of 0.05, analysis by intention-to-treat
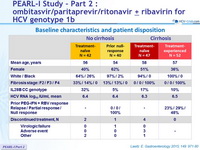
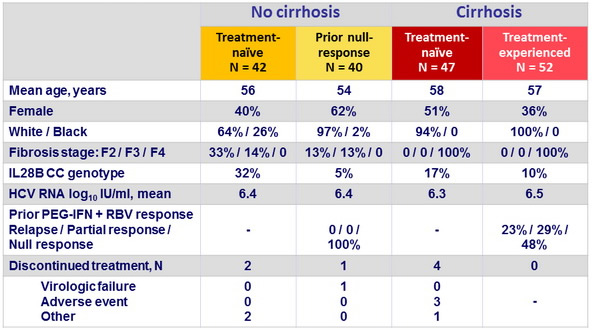
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition
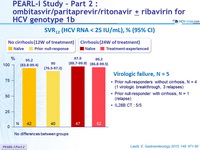
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/mL), % (95% CI)
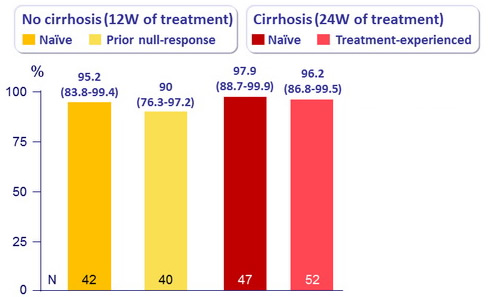
- No differences between groups
Virologic failure, N = 5
- Prior null-responders without cirrhosis, N = 4 (1 virologic breakthrough, 3 relapses)
- Prior null-responder with cirrhosis, N = 1 (relapse)
- IL28B CT : 5/5
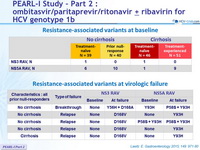
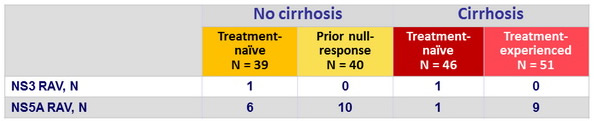
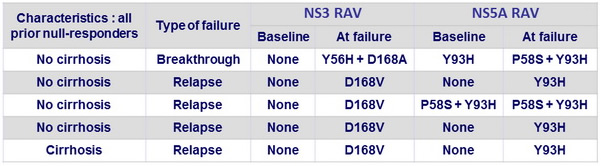
Resistance-associated variants at baseline
Resistance-associated variants at virologic failure
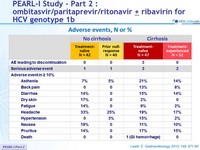
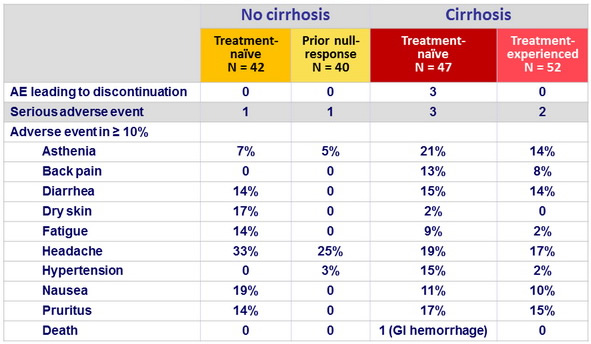
Adverse events, N or %
Summary
- An interferon - and ribavirin-free regimen of ombitasvir , paritaprevir , and ritonavir , achieved rates of SVR12 > 90% in patients with HCV genotype 1b infection with and without cirrhosis, with a 24-weeks or 12-weeks duration of treatment, respectively
- SVR12 was 95-98% in naïve patients
- SVR12 was 90-96% in treatment-experienced patients
- There were few virologic failures, all occurring in prior null responders (failure rate 5/65 = 7.6%), who also harbored CT IL28B genotype
- All 5 patients had NS3 and NS5A RAVs at failure
- The regimen was well tolerated and was associated with low rate (1.7%) of treatment discontinuation
- The majority of adverse events were mild in severity