C-EDGE Experienced Study: grazoprevir/elbasvir ± RBV in previous failure to PEG-IFN + RBV
Efficacy and Safety of Grazoprevir/Elbasvir +/- RBV for 12 Weeks in Patients with HCV G1 or G4 Infection who Previously Failed PEGINTERFERON/RBV: C-EDGE Treatment-Experienced TRIAL
Kwo P. Gastroenterology 2017;152:164-175; EASL 2015, Abs. P0886
Anti-HCV
Grazoprevir
Elbasvir
Grazoprevir
Elbasvir
Genotype
1
1a
1b
1
1a
1b
Treatment history
IFN-Experienced
IFN-Experienced
Cirrhosis
Yes
No
Yes
No
Design
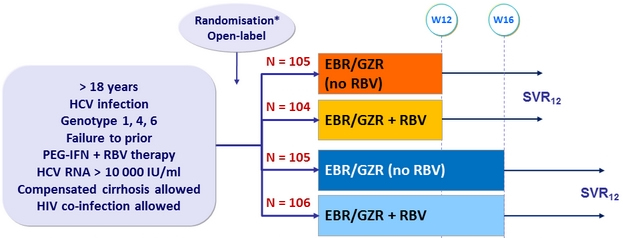
* Randomisation stratified on cirrhosis (yes or no) and response to prior PEG-IFN + RBV therapy (null response, partial response, relapse)
Grazoprevir (GZR) / Elbasvir (EBR ) 100/50 mg fixed dose combination : 1 tablet QD
Objective
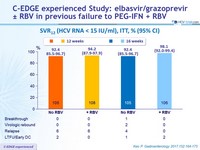
- SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml), with 95% CI, by intention to treat analysis, 99% power to demonstrate superiority to historical rate of 58%
Baseline characteristics and disposition
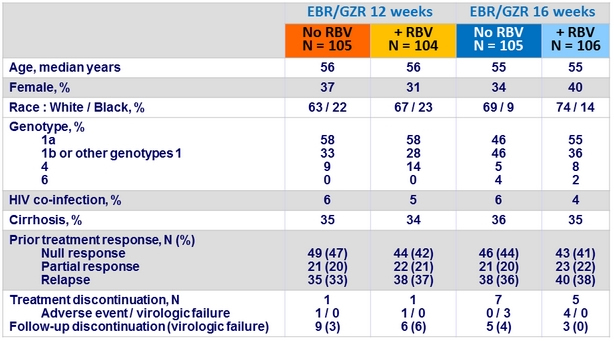
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml), ITT, % (95% CI)
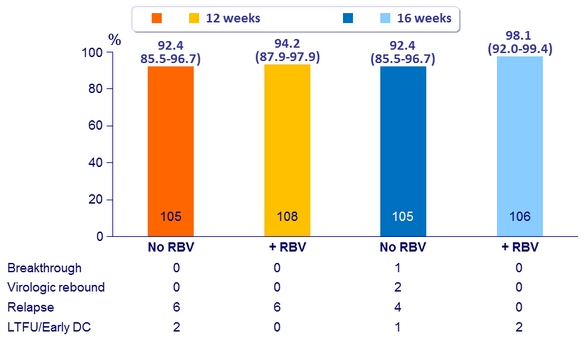
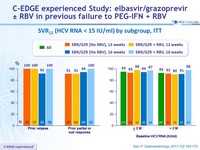
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) by subgroup, ITT, n/N (%)
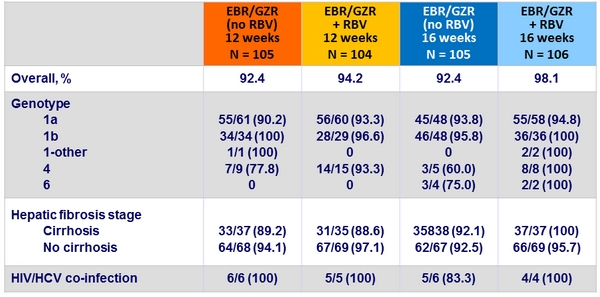
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) by subgroup, ITT
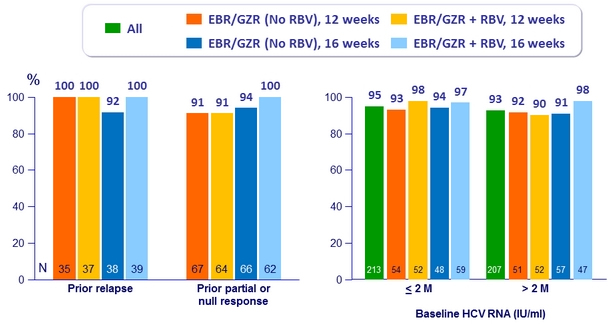
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 15 IU/ml) by subgroup, Per-protocol, n/N (%)
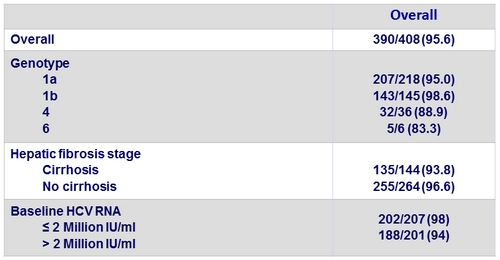
- The per-protocol analysis excluded 12 patients who discontinued for administrative reasons
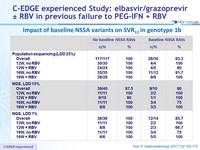
Resistance-Associated Variants
- Presence of NS3 RAVs at baseline in genotype 1 by population sequencing: 33.2% (123/170)
- NS3 variants at positions 36, 54, 55, 56, 80, 107, 122, 132, 155, 156, 158, 168, 170, and 175, considered for the analysis •
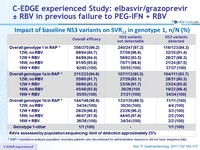
- SVR12 rates : 97.2% (240/247) and 94.3% (116/123) if baseline NS3 RAVs absent or present, respectively
- The slightly higher rate of virologic failure among patients with baseline NS3 RAVs is likely explained by the co-existence of baseline NS5A RAVs in these patients. Of the 14 virologic failures in genotype 1, 12 had baseline NS5A RAVs, and of the 2 failures who were wild-type for NS5A, only 1 had a baseline NS3 RAV
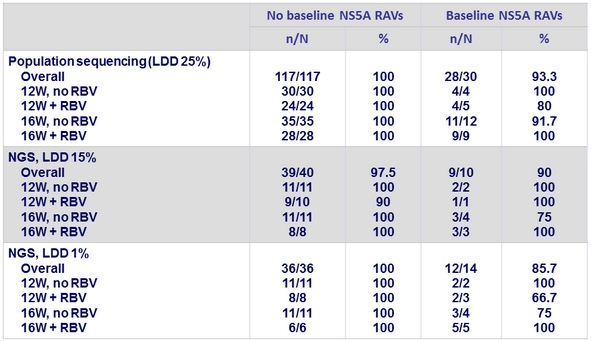
- NS5A RAVs at positions 28, 30, 31 and 93 assessed by population sequencing (limit of detection: 25%) and NGS (limit of detection:
1% and 15%)
- The lower-sensitivity assays (population sequencing and NGS 15%) offer the highest precision in identifying patients with baseline RAVs at risk of virologic failure
Impact of baseline NS3 variants on SVR12 in genotype 1, n/N (%)
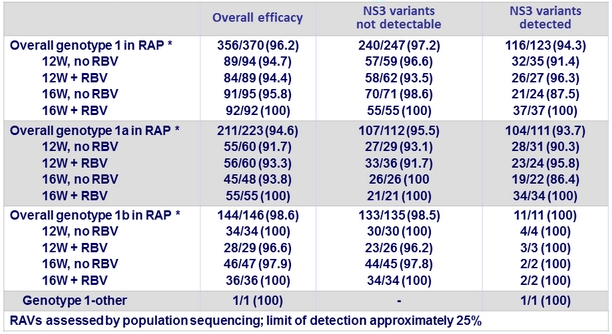
* RAP = resistance analysis population excludes patients who discontinued for administrative reasons or did not have
sequence data
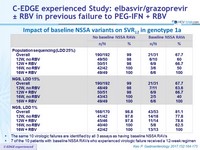
Impact of baseline NS5a variants on efficacy in genotype 1-infected subjects
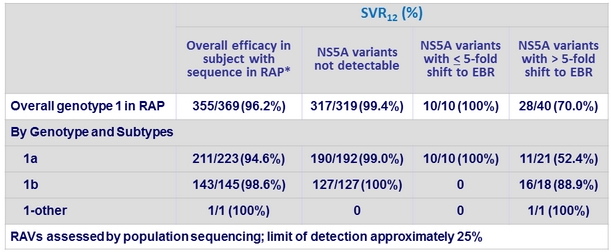
* RAP = resistance analysis population excludes patients who discontinued for administrative reasons or did not have sequence data
n/a = not applicable
Impact of baseline NS5a variants on SVR12 in genotype 1a
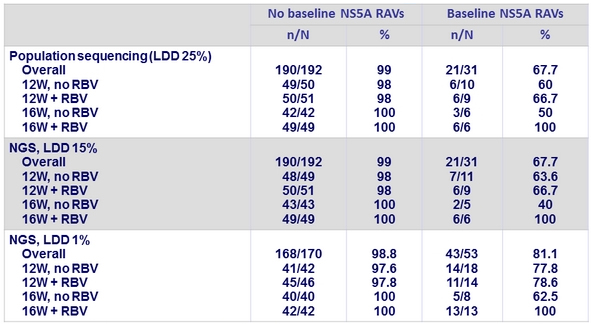
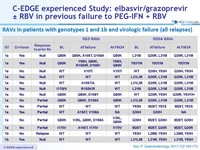
- The same 10 virologic failures are identified by all 3 assays as having baseline NS5A RAVs
- 7 of the 10 patients with baseline NS5A RAVs who experienced virologic failure received a 12-week regimen
Impact of baseline NS5a variants on SVR12 in genotype 1b
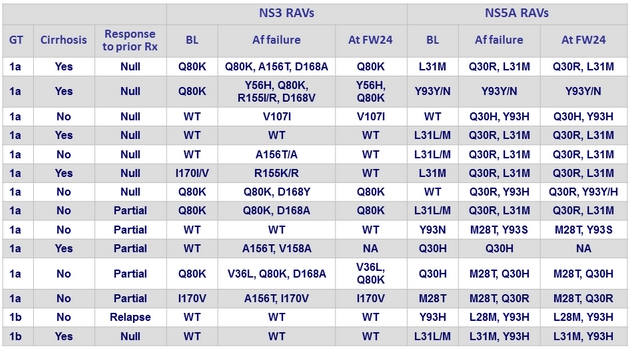
RAVs in patients with genotypes 1 and 1b and virologic failure (all relapses)
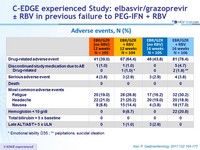
Adverse events, N (%)
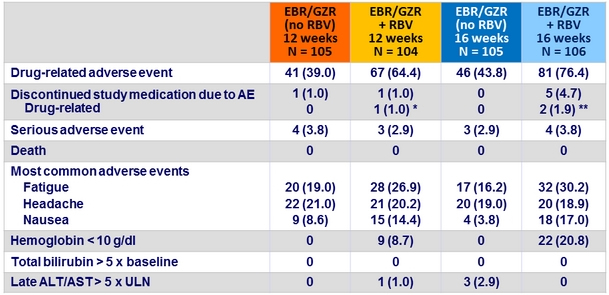
* Emotional lability D35 ; ** palpitations, suicidal ideation
Summary
- In patients who failed prior PEG-IFN + RBV therapy
- 12 weeks of EBR/GZR without RBV achieved SVR12 in 100 % of patients with history of relapse to prior PEG-IFN + RBV
- 12 weeks of EBR/GZR without RBV achieved SVR12 in 100% of genotype 1b
- 16 weeks of EBR/GZR + RBV achieved SVR 12 of 100% with no virologic failure regardless of prior treatment history or cirrhosis status or NS5A RAV
- There was no difference in response rates between patients with and without cirrhosis, irrespective of therapy duration and with or without the addition of RBV
- Of the 12 genotype 1a with virologic failure, 10 had a baseline NS5A RAV
- EBR/GZR FDC was generally safe and well tolerated
- Virologic failure was seen in 5.8% of patients treated with 12W of EBR/GZR
- To maximize SVR rates, genotype 1a or 4-infected patients with a prior history of null or partial response to PEG-IFN + RBV
- may benefit from the addition of RBV and extension of therapy to 16 weeks,
- alternatively, baseline RAV testing of genotype 1a-infected patients may be used to identify the small subset of patients who can benefit from the addition of RBV and extension of therapy to 16 weeks