C-212 Study: SMV + PEG-IFN + RBV for genotype 1 in HIV co-infection
Simeprevir (TMC435) With Pegylated Interferon/Ribavirin in Patients Coinfected With HCV Genotype 1 and HIV-1: A Phase 3 Study
Dieterich D. CID 2014;59:1579-87
Anti-HCV
Simeprevir
PEG-IFNα 2a
Ribavirin
Simeprevir
PEG-IFNα 2a
Ribavirin
Genotype
1
1a
1b
1
1a
1b
Treatment history
Naive
Naive
Cirrhosis
Yes
No
Yes
No
Special population
HIV co-infection
HIV co-infection
Design
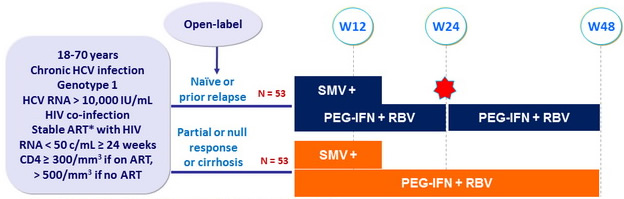
*
Permitted ART : 3TC/FTC, ABC, TDF, RPV, RAL, MVC
SMV 150 mg : 1 pill qd ; PEG-IFNα-2a : 180 m g SC once weekly
RBV : 1000 or 1200 mg/day (bid dosing) according to body weight (< or = 75 kg)
- Response-guided therapy : Patients with HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml at W4 and < 15 IU/ml at W12 stopped treatment at W24, otherwise they continued until W48
- Virological stopping rules : SMV discontinued if HCV RNA >1000 IU/ mL at W4 or W12, or if HCV RNA confirmed = 25 IU/ mL at W24 or W36
Objective
- SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/mL) by intention to treat
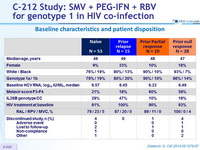
Baseline characteristics and patient disposition
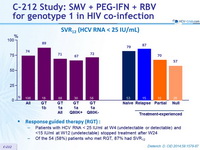
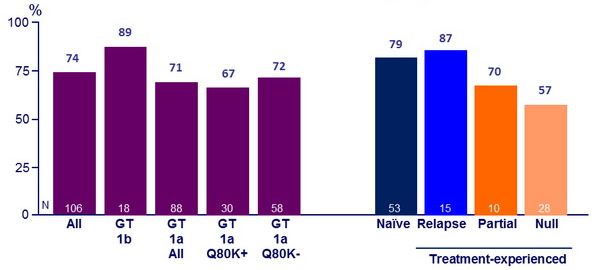
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ mL)
Response guided therapy (RGT)
- Patients with HCV RNA < 25 IU/ml at W 4 (undetectable or detectable) and <15 IU/ml at W 12 (undetectable) stopped treatment after W24
- Of the 54 (58%) patients who met RGT, 87% had SVR12
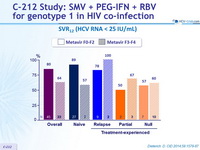
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ mL)
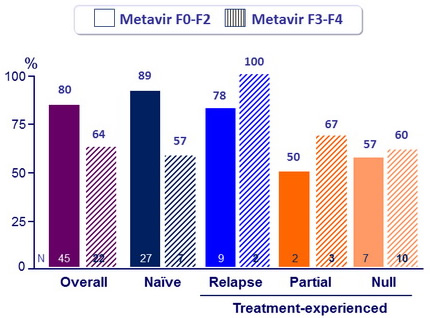
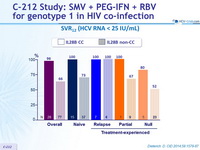
SVR12 (HCV RNA < 25 IU/ mL)
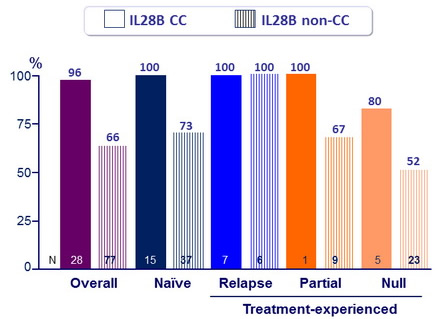
Virologic failure
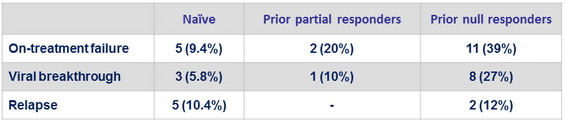
Emergence of resistance
- Paired baseline and failure NS3 sequencing in 26/29 failure
- Emergence of NS3 mutations in 25/26 (96%)
HIV endpoints
- Confirmed failure : 2/93 (2.2%) of patients on antiretroviral therapy ; both had SVR12
Adverse events
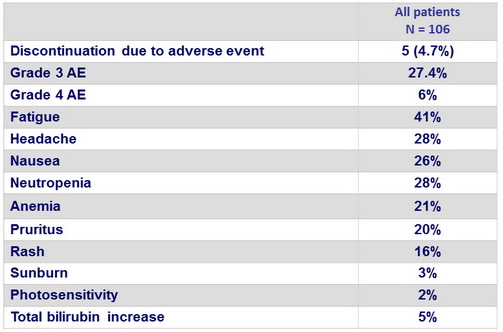
Summary
- Oral, once-daily treatment with SMV 150 mg for 12 weeks plus PEG-IFN + RBV for either 24 or 48 weeks led to high rates of SVR12 in patients with HCV genotype 1 and HIV-1 coinfection , regardless of prior HCV treatment response
- Most eligible patients met response-guided therapy criteria enabling a shorter, 24-week overall duration of PEG-IFN + RBV therapy
- SMV was generally well tolerated, with safety similar to that reported in larger studies in patients without HIV coinfection
- Limitations
- No control arm